
WordPress is a free and open-source content management system (CMS). It’s the simplest and most popular solution to create your own website or blog. WordPress makes building a website accessible to anyone, even people who aren’t developers. With WordPress you can create any type of website such as blogs, eCommerce stores, portfolio websites, forums, resumes, business websites etc. In this step by step guide I will show you how to install WordPress on your Synology NAS using Docker & Portainer. Note: Make sure your NAS model supports AVX.
STEP 1
Please Support My work by Making a Donation.
STEP 2
Install Text Editor via Synology “Package Center”. (Mandatory STEP.) If you already have Text Editor installed on your Synology NAS, skip this STEP.
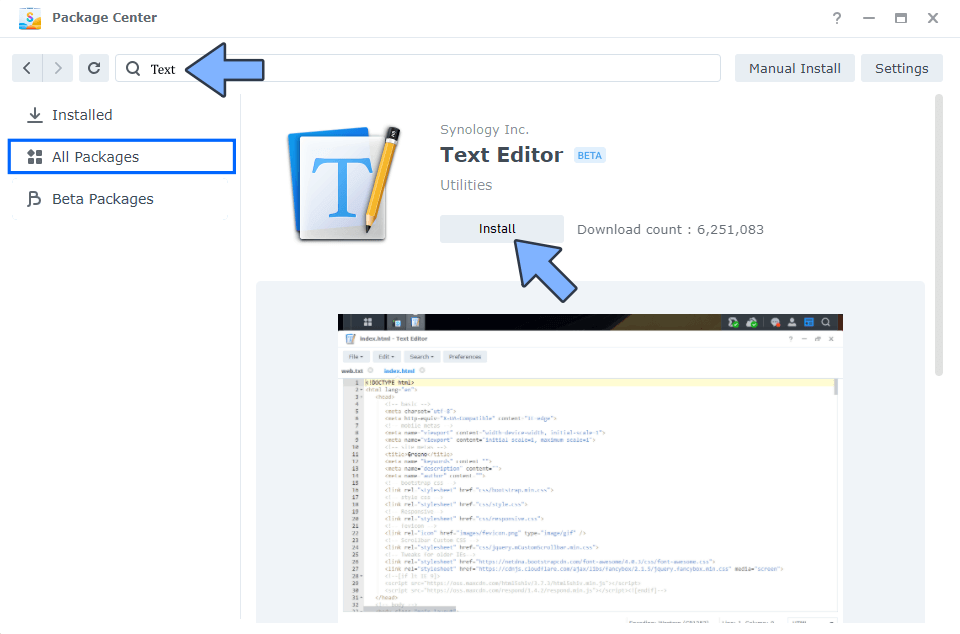
STEP 3
Install Portainer using my step by step guide. If you already have Portainer installed on your Synology NAS, skip this STEP. Attention: Make sure you have installed the latest Portainer version.
STEP 4
Make sure you have a synology.me Wildcard Certificate. Follow my guide to get a Wildcard Certificate. If you already have a synology.me Wildcard certificate, skip this STEP.
STEP 5
Go to Control Panel / Login Portal / Advanced Tab / click Reverse Proxy. Follow the instructions in the image below.
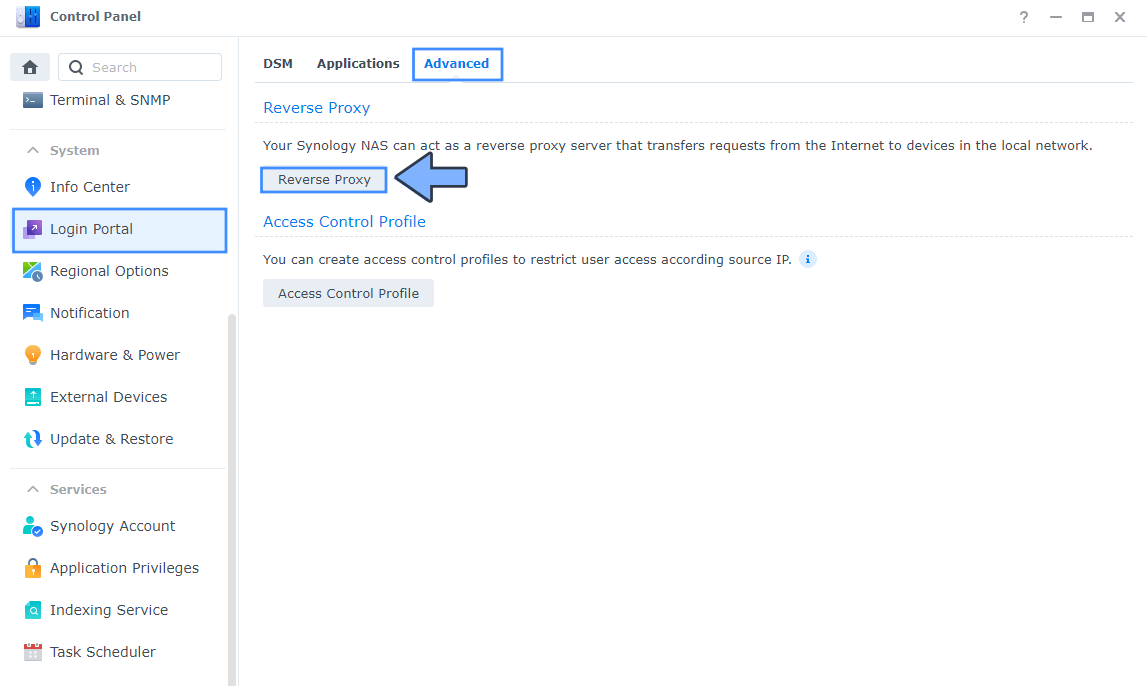
STEP 6
Now click the “Create” button. Follow the instructions in the image below.
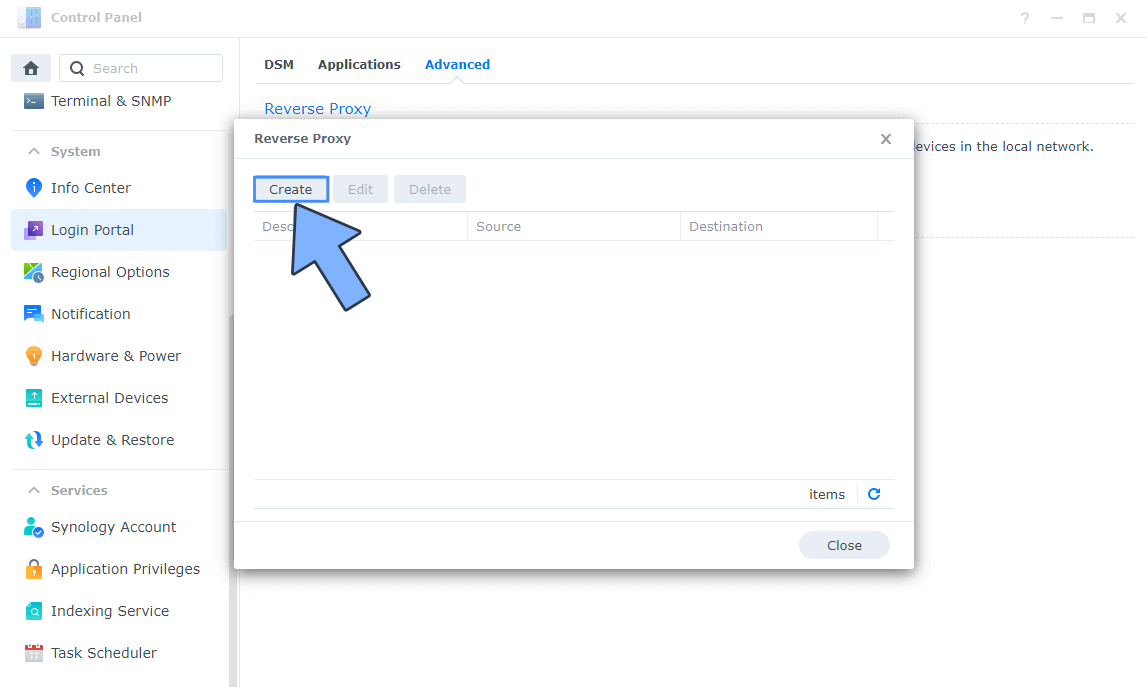
STEP 7
After you click the Create button, the window below will open. Follow the instructions in the image below.
On the General area, set the Reverse Proxy Name description: type in WordPress. After that, add the following instructions:
Source:
Protocol: HTTPS
Hostname: wordpress.yourname.synology.me
Port: 443
Check Enable HSTS
Destination:
Protocol: HTTP
Hostname: localhost
Port: 8195
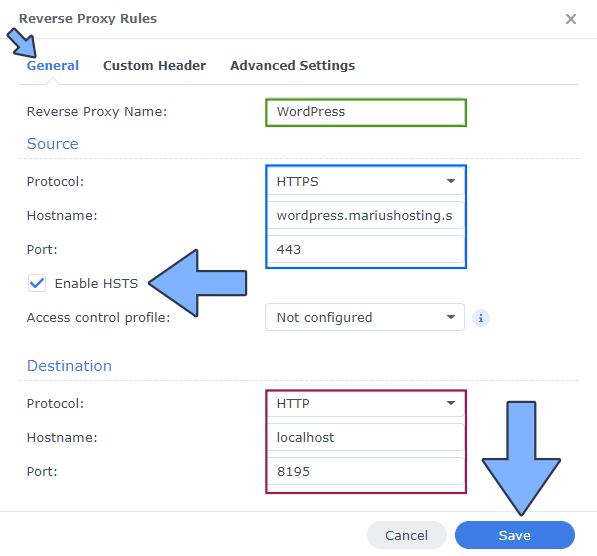
STEP 8
On the Reverse Proxy Rules click the Custom Header tab. Click Create and then, from the drop-down menu, click WebSocket. After you click on WebSocket, two Header Names and two Values will be automatically added. Click Save. Follow the instructions in the image below.
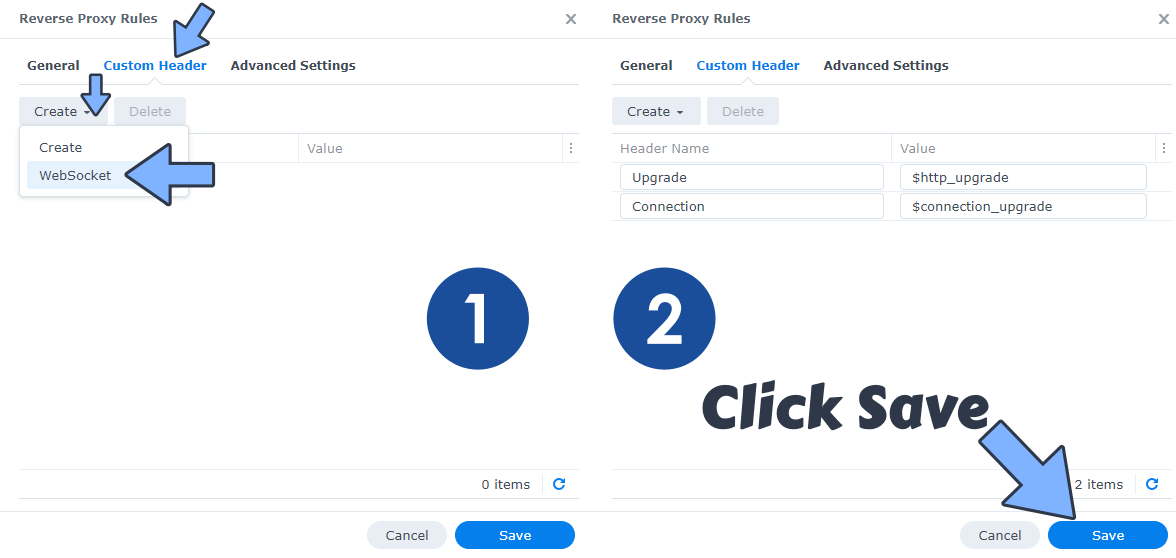
STEP 9
Go to Control Panel / Network / Connectivity tab/ Check Enable HTTP/2 then click Apply. Follow the instructions in the image below.
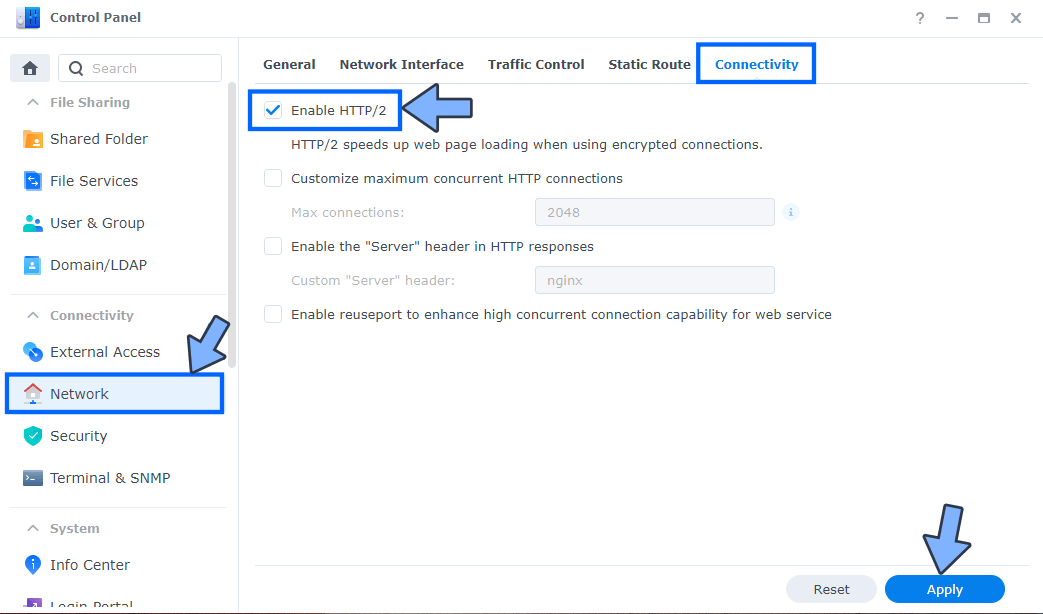
STEP 10
Go to Control Panel / Security / Advanced tab/ Check Enable HTTP Compression then click Apply. Follow the instructions in the image below.
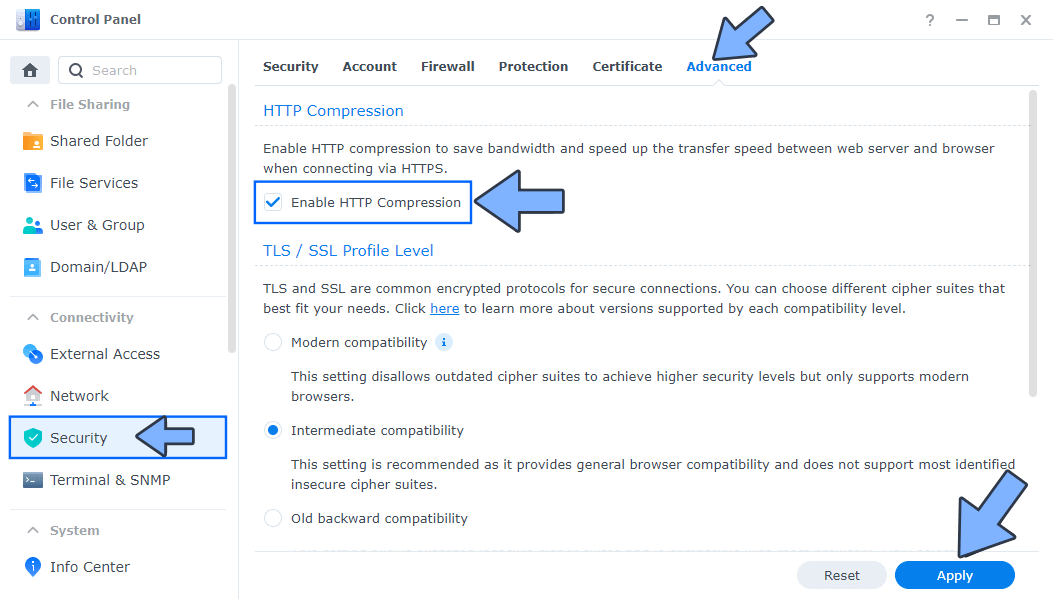
STEP 11
Go to File Station and open the docker folder. Inside the docker folder, create one new folder and name it wordpress. Follow the instructions in the image below.
Note: Be careful to enter only lowercase, not uppercase letters.
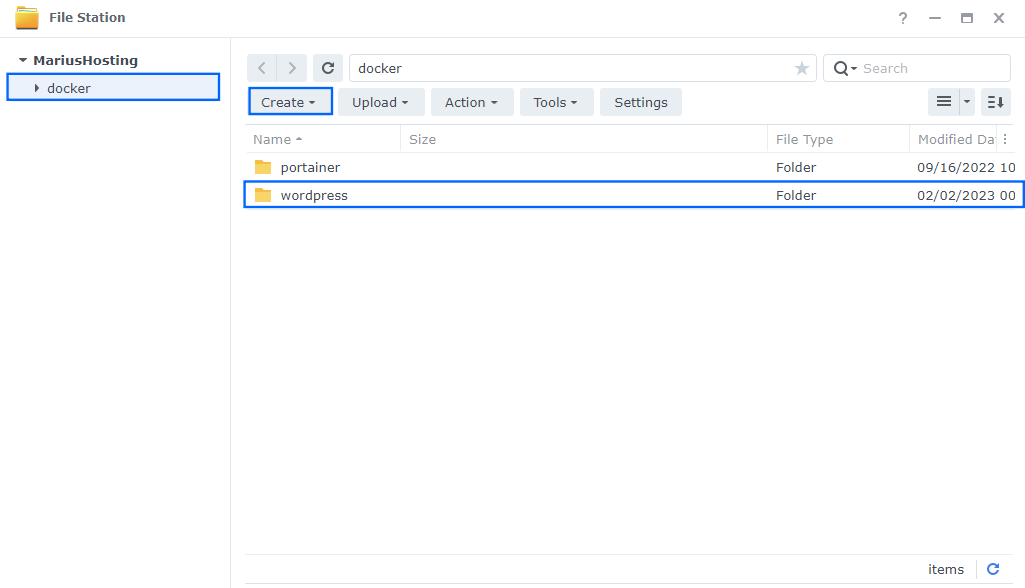
STEP 12
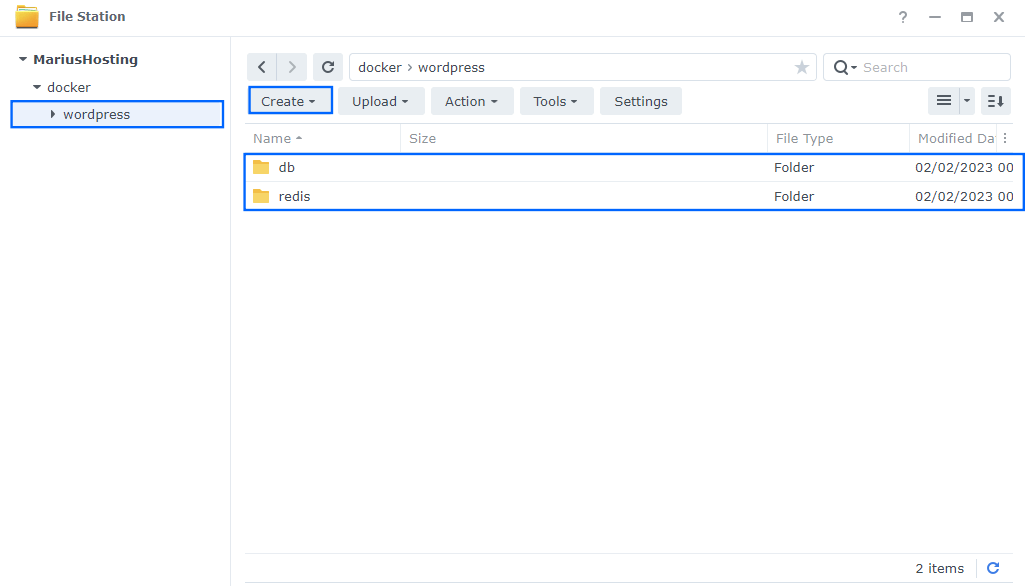
Now create two new folders inside the wordpress folder that you created at STEP 11 and name them db and redis. Follow the instructions in the image below.
Note: Be careful to enter only lowercase, not uppercase letters.
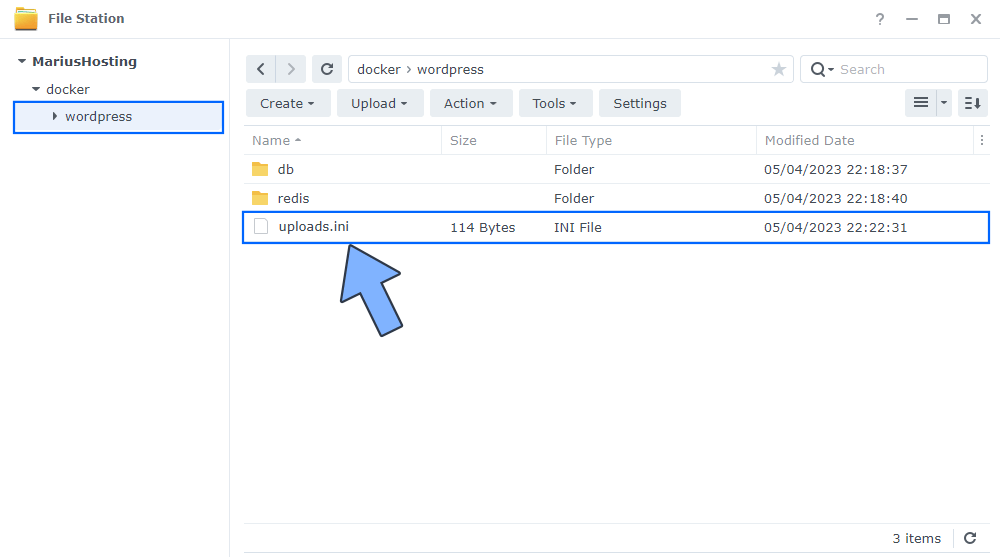
STEP 13
Download (click on the blue link below) then unzip and upload the uploads.ini file below in the wordpress folder that you have previously created at STEP 11. Follow the instructions in the image below. 🔒Note: Support my work to unlock the password. You can use this password to download any file on mariushosting forever!
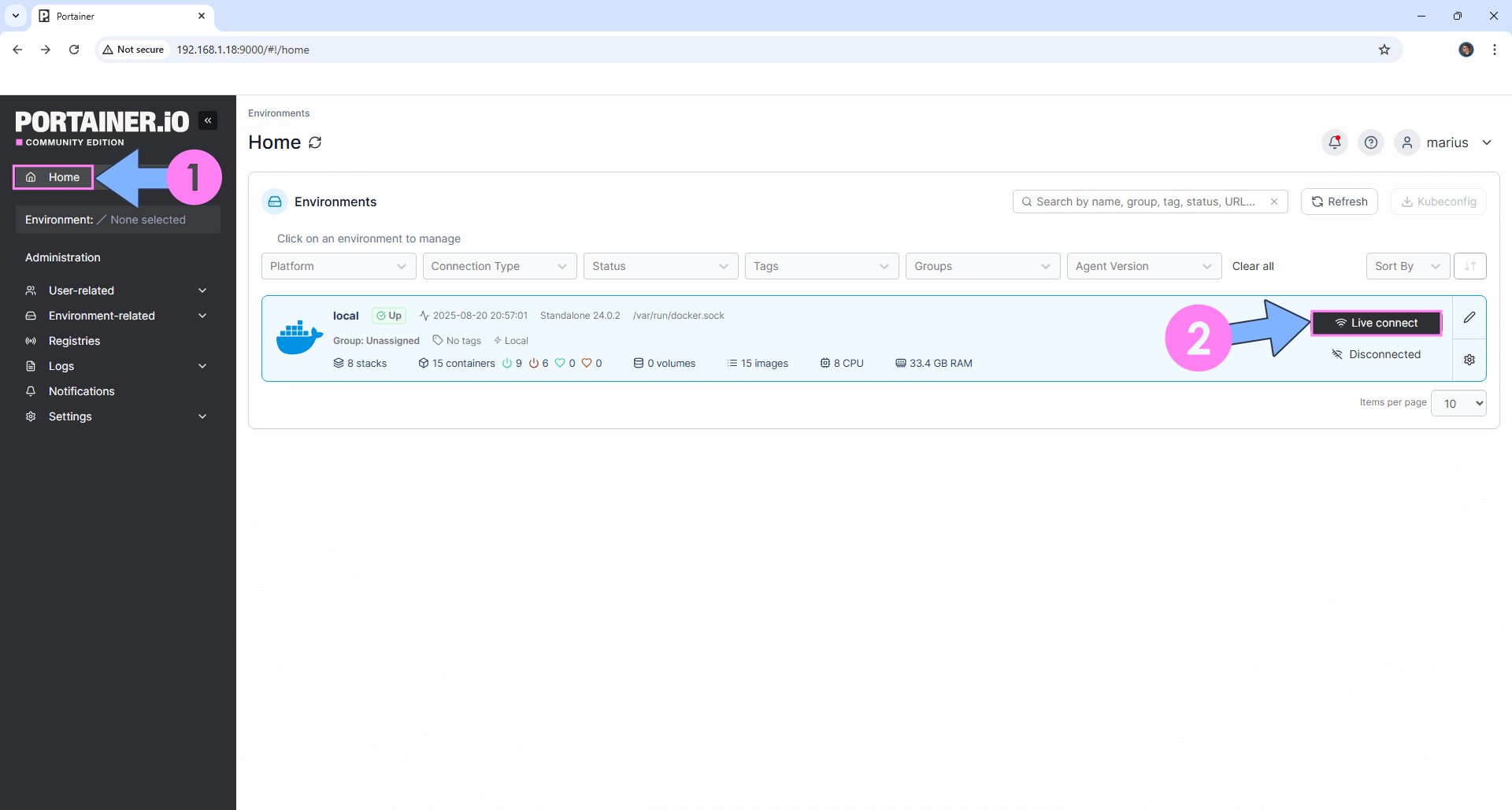
STEP 14
Log into Portainer using your username and password. On the left sidebar in Portainer, click on Home then Live connect. Follow the instructions in the image below.
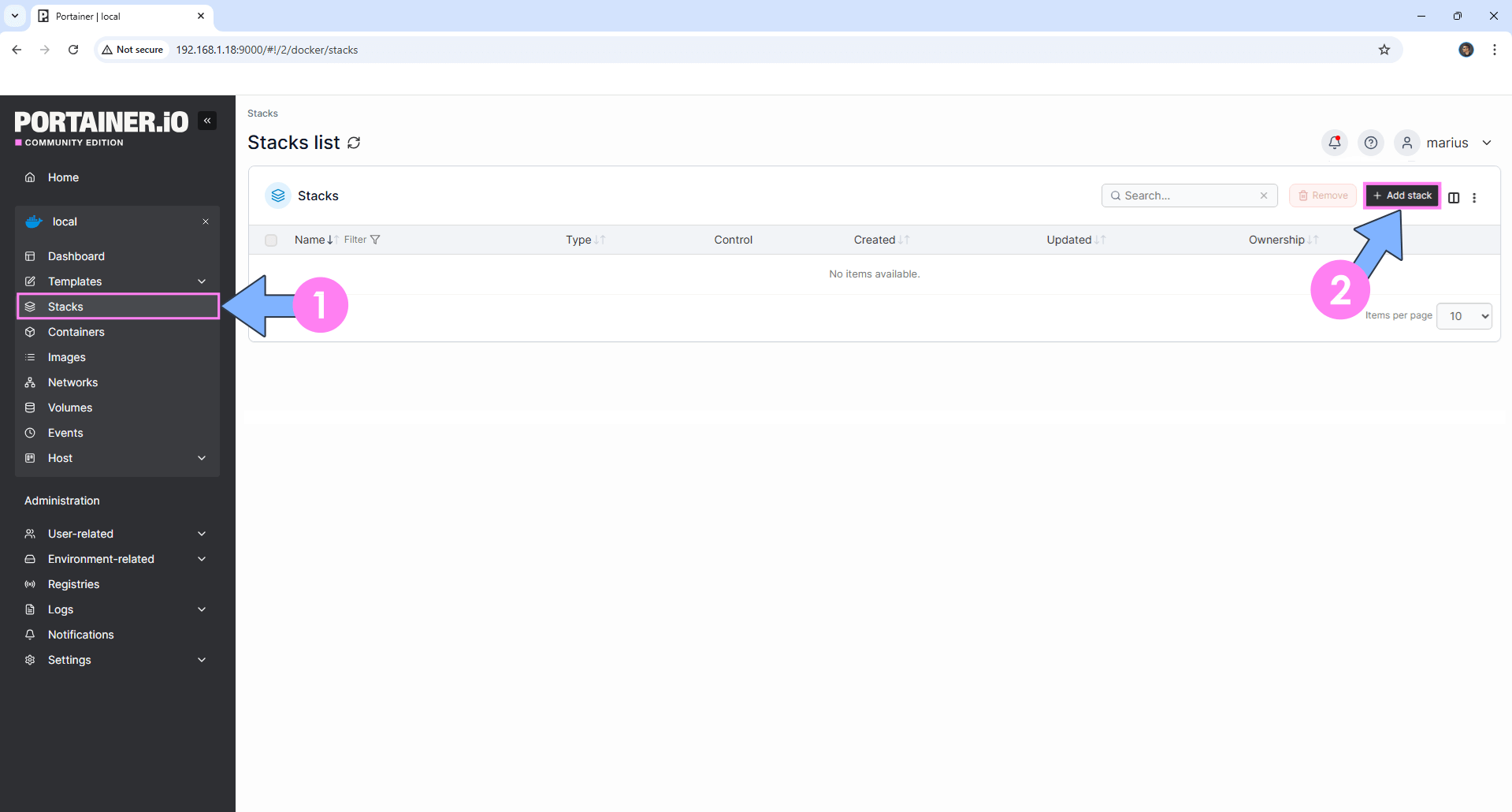
On the left sidebar in Portainer, click on Stacks then + Add stack. Follow the instructions in the image below.
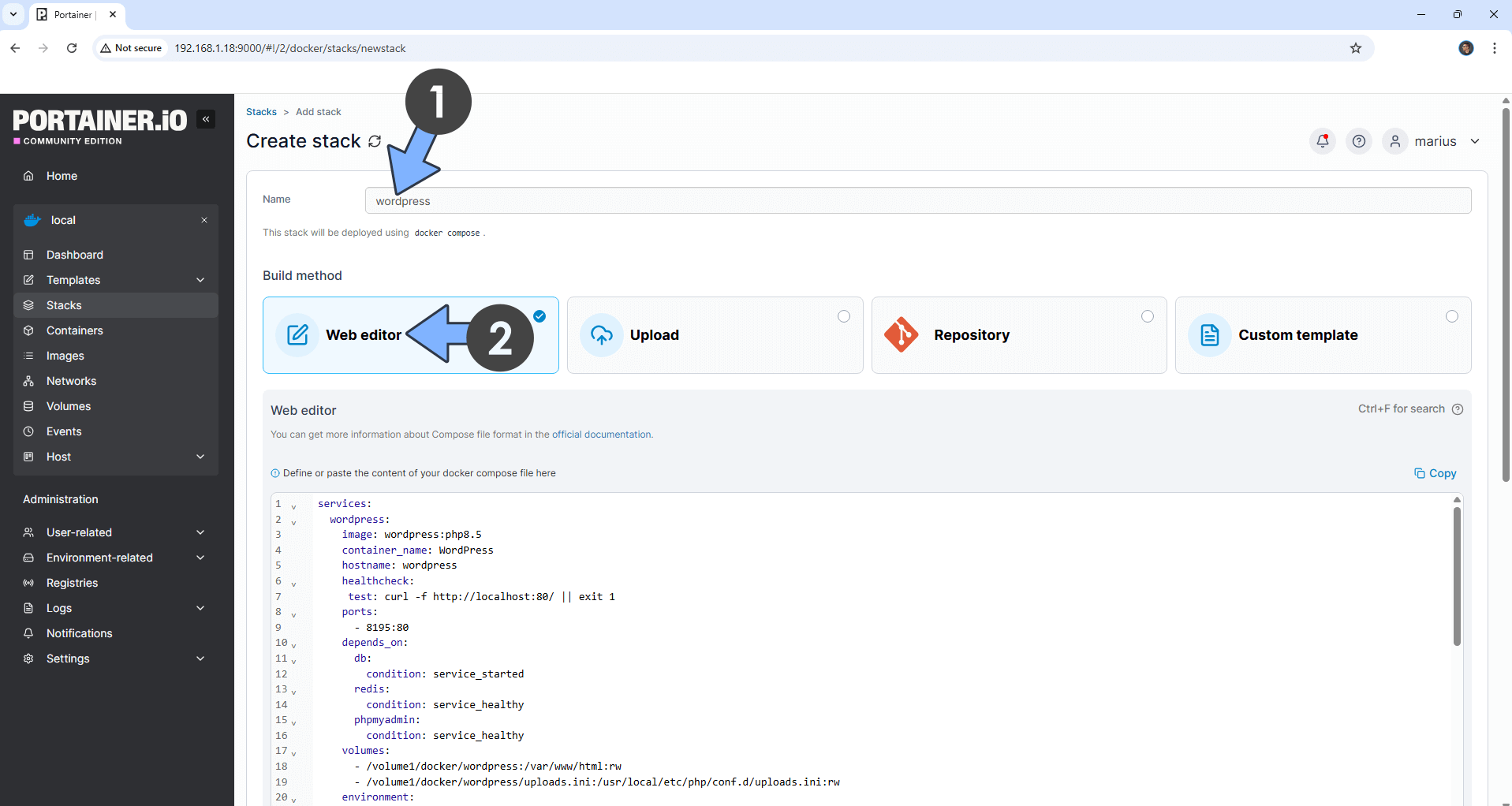
STEP 15
In the Name field type in wordpress. Follow the instructions in the image below.
services:
wordpress:
image: wordpress:php8.5
container_name: WordPress
hostname: wordpress
healthcheck:
test: curl -f http://localhost:80/ || exit 1
ports:
- 8195:80
depends_on:
db:
condition: service_started
redis:
condition: service_healthy
phpmyadmin:
condition: service_healthy
volumes:
- /volume1/docker/wordpress:/var/www/html:rw
- /volume1/docker/wordpress/uploads.ini:/usr/local/etc/php/conf.d/uploads.ini:rw
environment:
WORDPRESS_DB_HOST: db
WORDPRESS_DB_USER: marius
WORDPRESS_DB_PASSWORD: mariuspassword
WORDPRESS_DB_NAME: mariushosting_db
restart: on-failure:5
db:
image: mariadb:11.8-noble #LTS Long Time Support Until October 15, 2033.
container_name: WordPress-DB
security_opt:
- no-new-privileges:true
hostname: wordpress-db
environment:
MYSQL_DATABASE: mariushosting_db
MYSQL_USER: marius
MYSQL_PASSWORD: mariuspassword
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: rootpass
TZ: Europe/Bucharest
volumes:
- /volume1/docker/wordpress/db:/var/lib/mysql:rw
restart: on-failure:5
redis:
image: redis
hostname: wordpress-redis
container_name: WordPress-REDIS
user: 1026:100
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD-SHELL", "redis-cli ping || exit 1"]
volumes:
- /volume1/docker/wordpress/redis:/data:rw
environment:
TZ: Europe/Bucharest
restart: on-failure:5
phpmyadmin:
image: phpmyadmin
hostname: wordpress-phpmyadmin
healthcheck:
test: curl -f http://localhost:80/ || exit 1
container_name: WordPress-phpMyAdmin
ports:
- 2500:80
environment:
PMA_HOST: wordpress-db
PMA_PORT: 3306
restart: on-failure:5Note: Before you paste the code above in the Web editor area below, change the values for WORDPRESS_DB_USER and MYSQL_USER. Type in your own username for both values; they have to be identical. marius is an example for a user.
Note: Before you paste the code above in the Web editor area below, change the value for WORDPRESS_DB_PASSWORD and MYSQL_PASSWORD. Type in your own password for both values; they have to be identical. mariuspassword is an example for a password. ⚠️Warning: Do NOT use a password with special characters that include the dollar symbol $.
Note: Before you paste the code above in the Web editor area below, change the value for WORDPRESS_DB_NAME and MYSQL_DATABASE. Type in your own database name for both values; they have to be identical. mariushosting_db is an example for a database name.
Note: Before you paste the code above in the Web editor area below, change the value for TZ. (Select your current Time Zone from this list.)
Note: Before you paste the code above in the Web editor area below, change the value numbers for user with your own UID and GID values. (Follow my step by step guide on how to do this.) 1026 is my personal UID value and 100 is my personal GID value. You have to type in your own values.
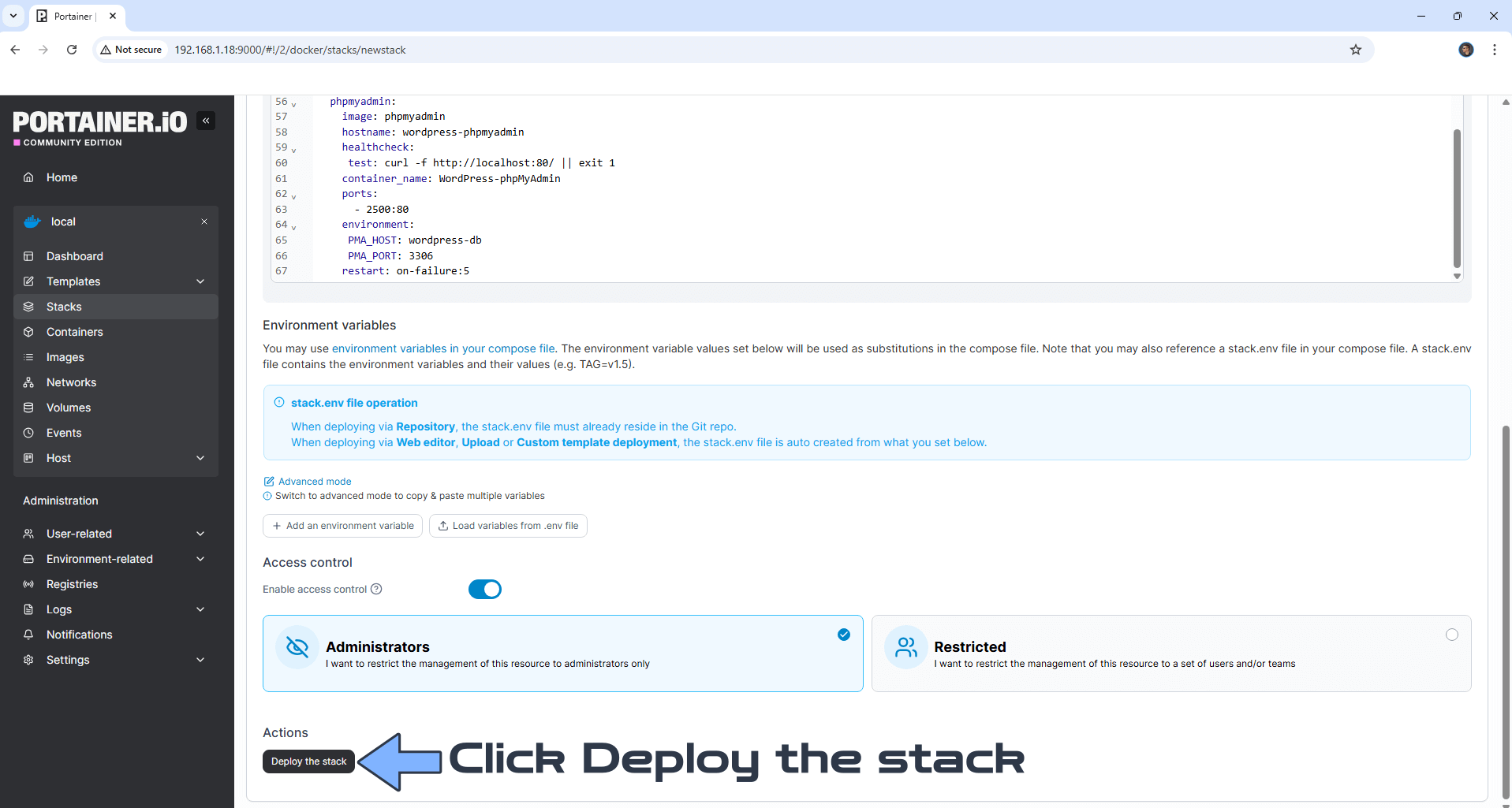
STEP 16
Scroll down on the page until you see a button named Deploy the stack. Click on it. Follow the instructions in the image below. The installation process can take up to a few minutes. It will depend on your Internet speed connection.
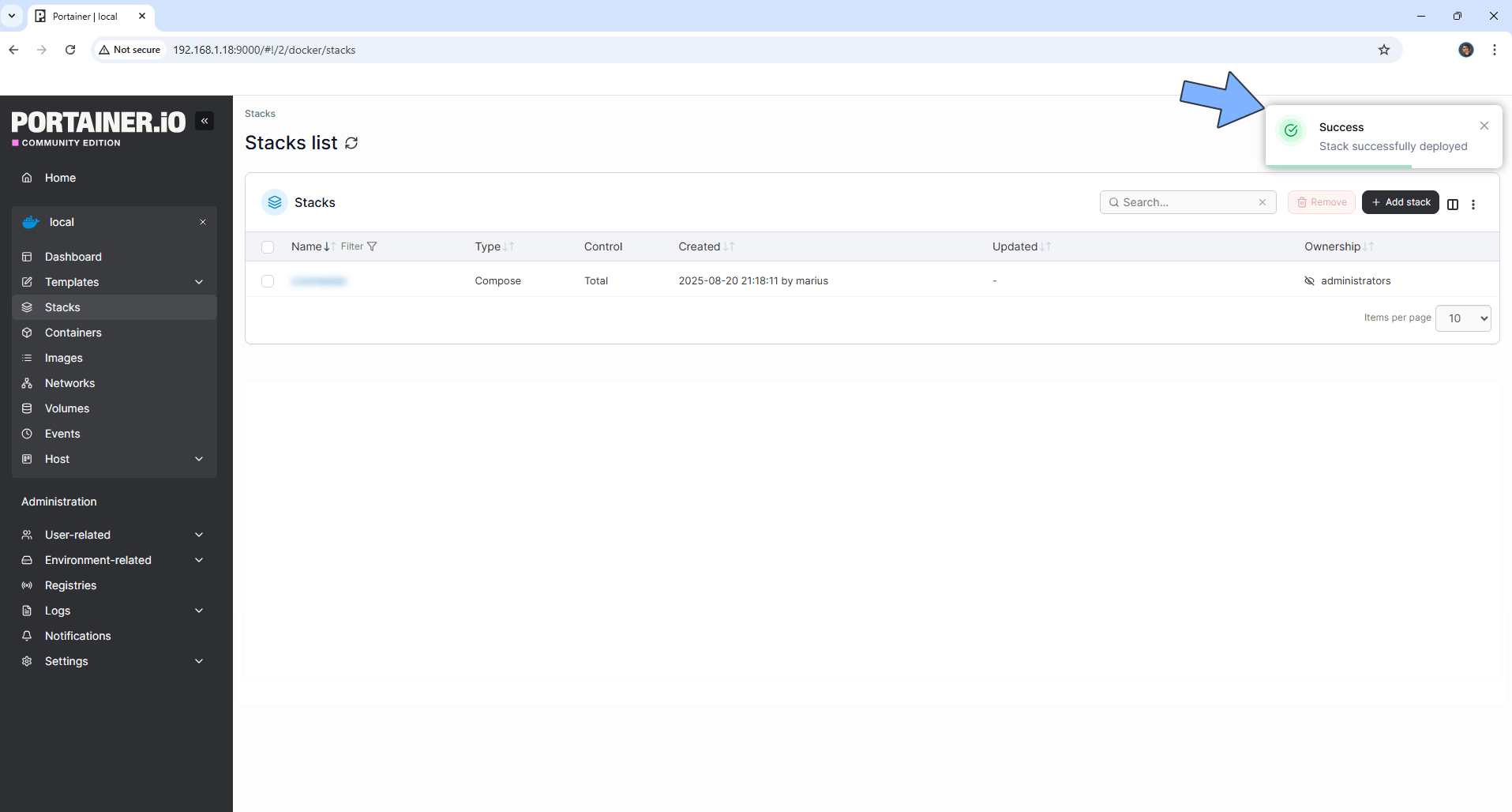
STEP 17
If everything goes right, you will see the following message at the top right of your screen: “Success Stack successfully deployed“.
STEP 18
🟢Please Support My work by Making a Donation. Almost 99,9% of the people that install something using my guides forget to support my work, or just ignore STEP 1. I’ve been very honest about this aspect of my work since the beginning: I don’t run any ADS, I don’t require subscriptions, paid or otherwise, I don’t collect IPs, emails, and I don’t have any referral links from Amazon or other merchants. I also don’t have any POP-UPs or COOKIES. I have repeatedly been told over the years how much I have contributed to the community. It’s something I love doing and have been honest about my passion since the beginning. But I also Need The Community to Support me Back to be able to continue doing this work.
STEP 19
Please wait approximately 5 minutes for the installation to be completed or you will get a blank page with the following error message: Error establishing a database connection. Now open your browser and type in your HTTPS/SSL certificate like this https://wordpress.yourname.synology.me In my case it’s https://wordpress.mariushosting.synology.me If everything goes right, you will see the WordPress Installation Page. Choose your language then click Continue. Follow the instructions in the image below.
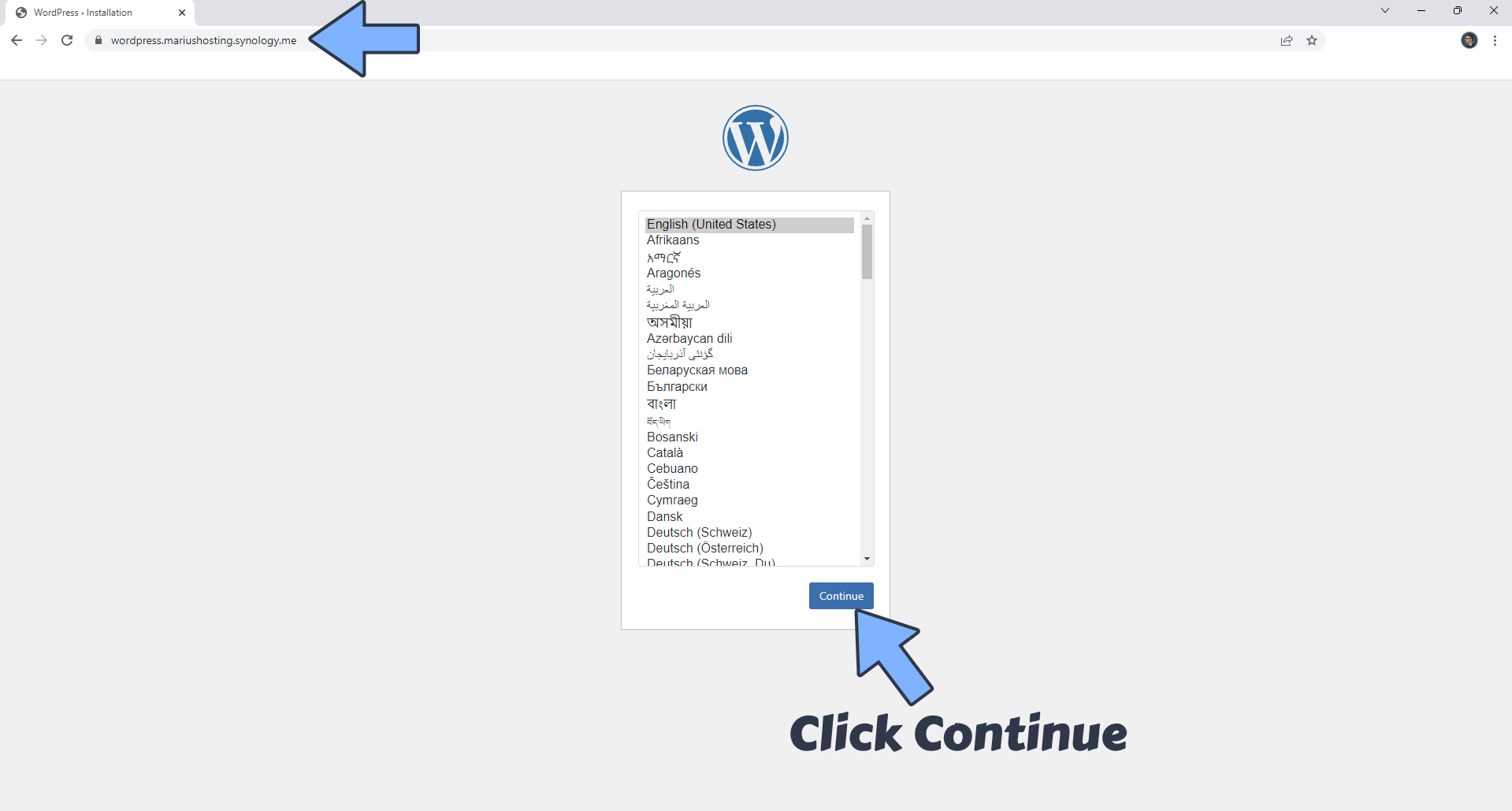
STEP 20
Type in your Site title, your own Username, your own Password and your own Email then click Install WordPress. Follow the instructions in the image below. ⚠️Warning: Username and Password in this area should be created now. ⚠️Do not confuse this Username and Password with the ones created at STEP 15.
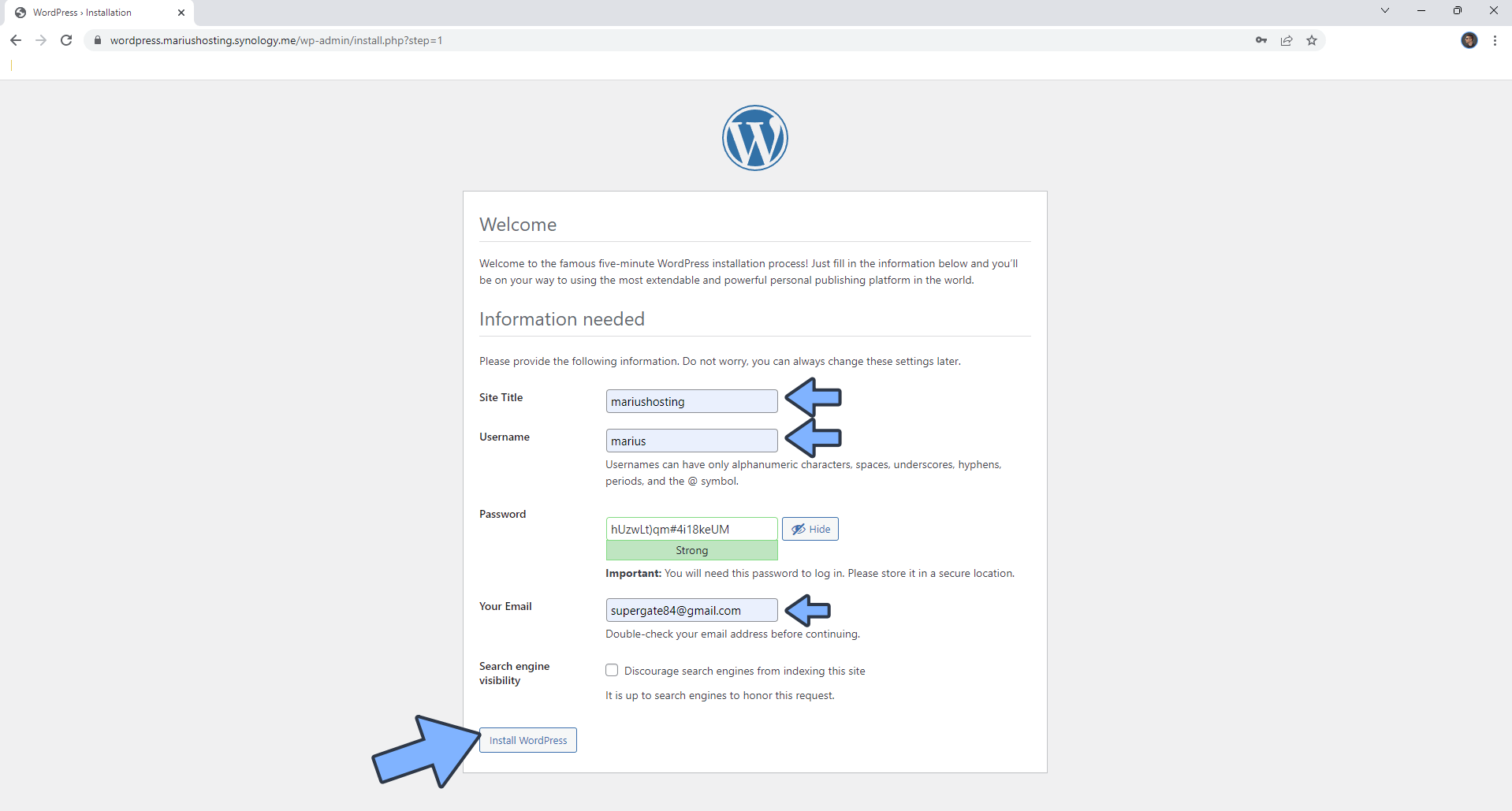
STEP 21
Wait approximately 1 minute for the installation to be completed. Click Log in. Follow the instructions in the image below.
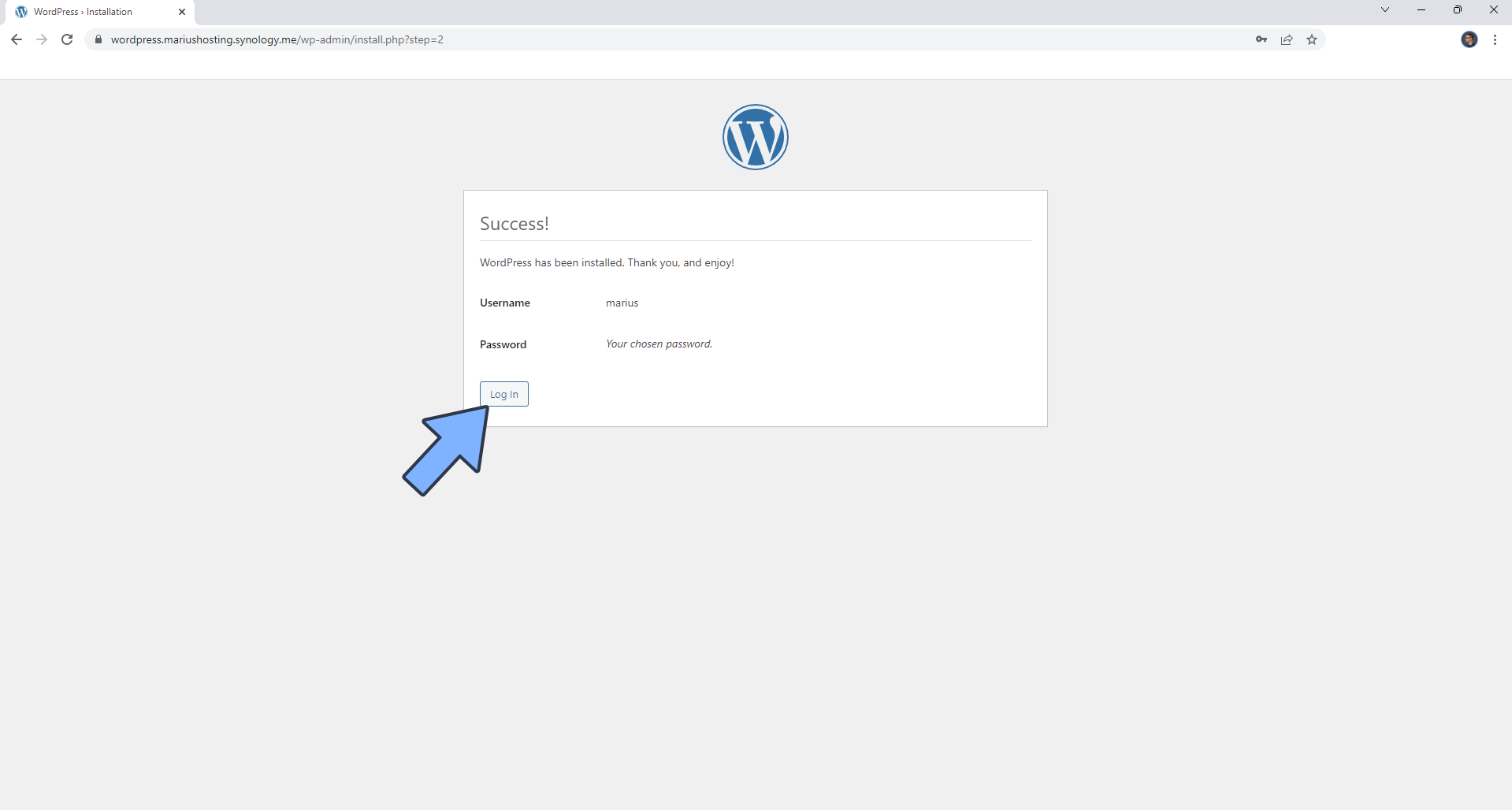
STEP 22
Type in your own Username and Password that you have previously created at STEP 20 then click Log in. Follow the instructions in the image below.
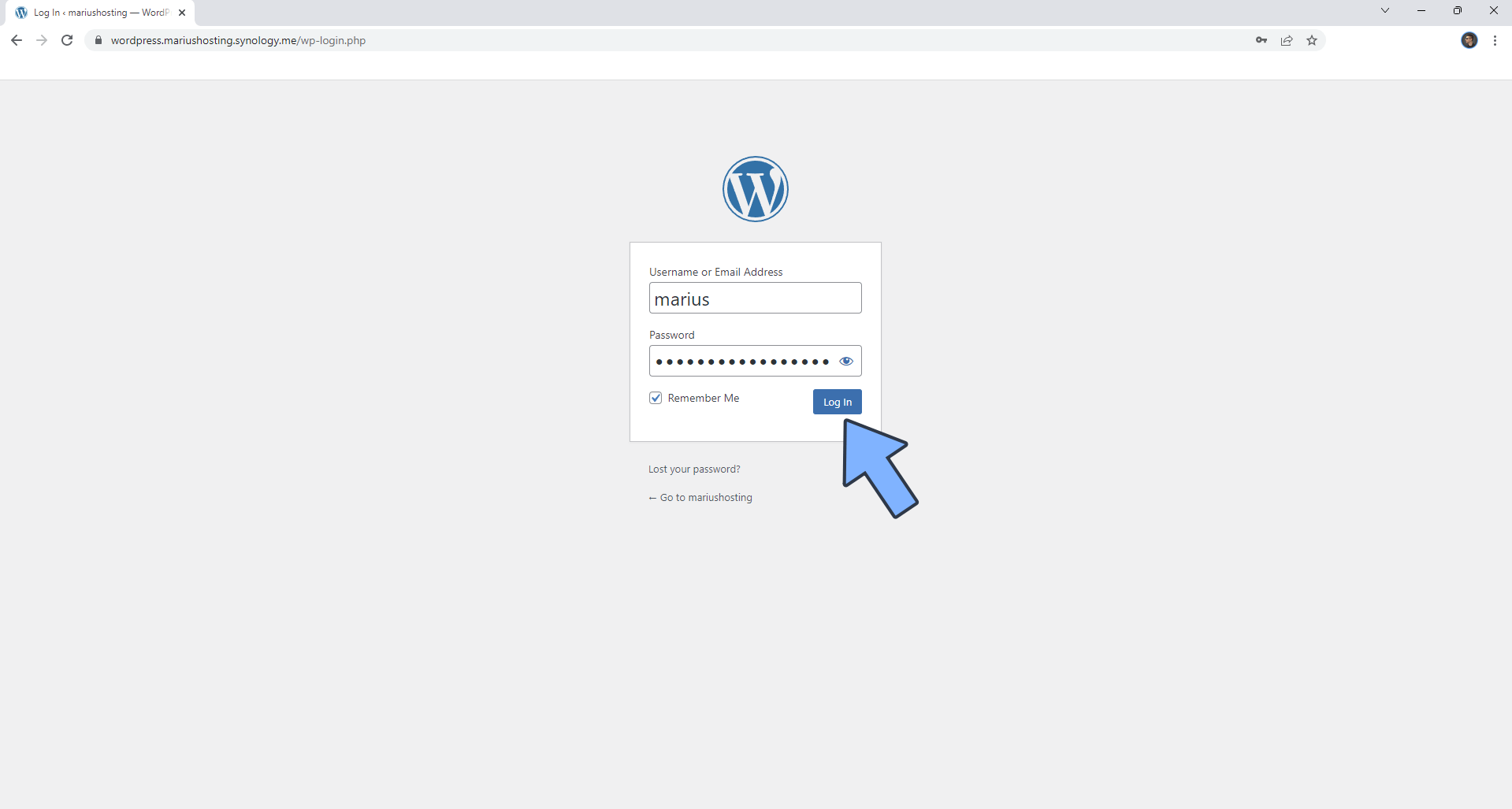
STEP 23
Your WordPress instance should look like this.
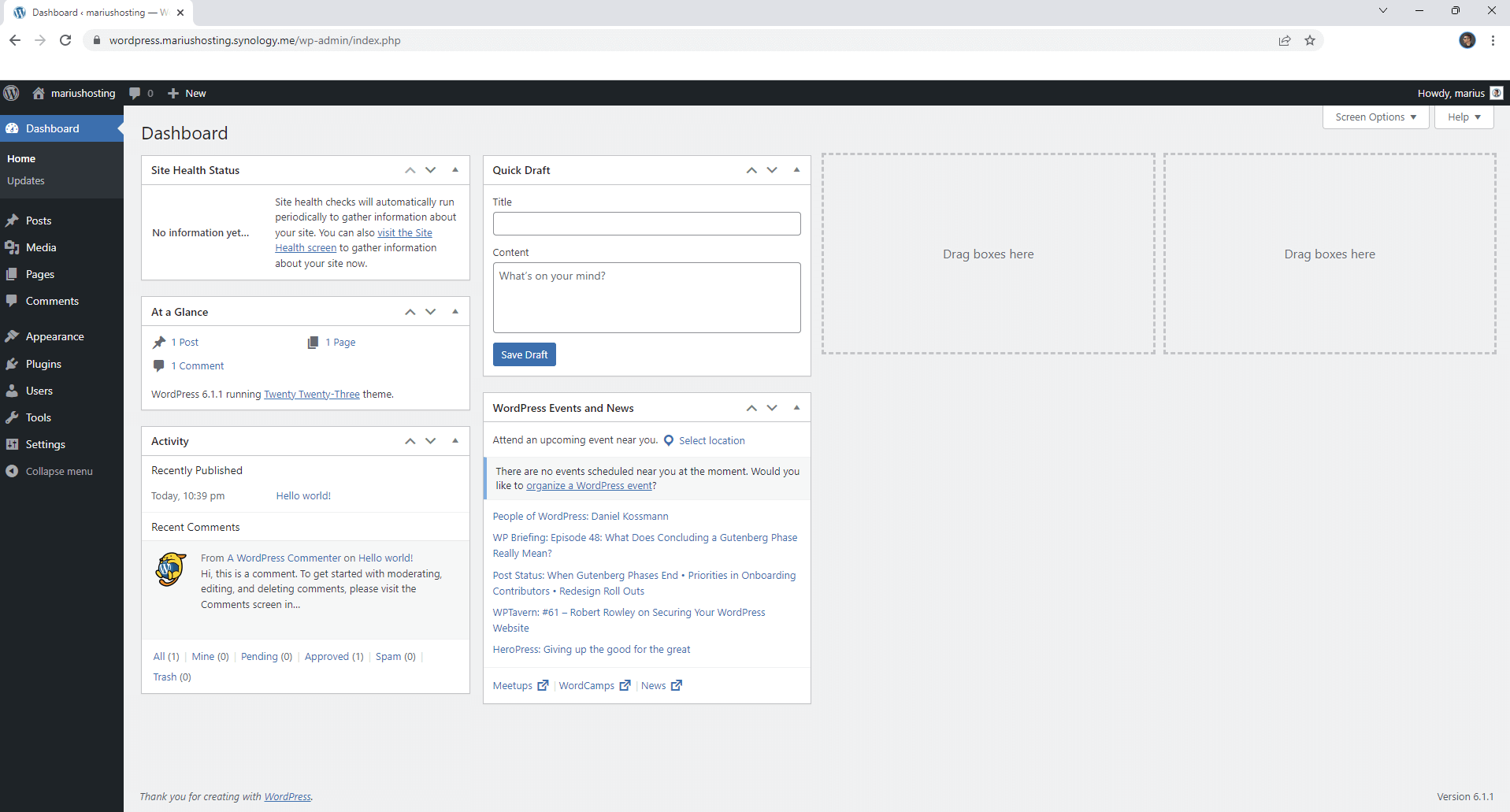
STEP 24
Go to File Station then open the wordpress folder. Follow the instructions in the image below.
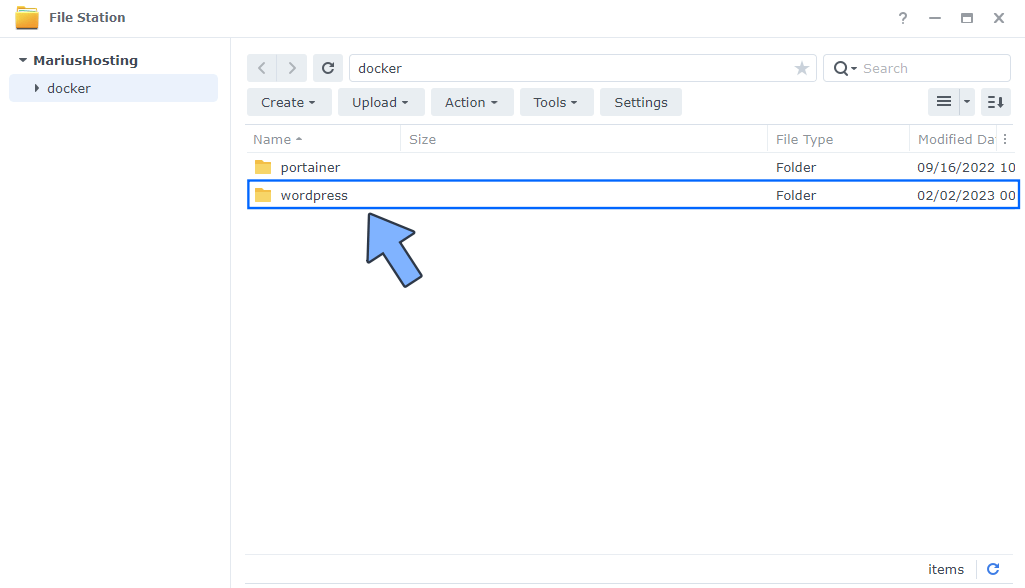
STEP 25
Make sure you have installed Synology Text Editor as per the instructions at STEP 2. Double click on the wp-config.php file to open it. Follow the instructions in the image below.
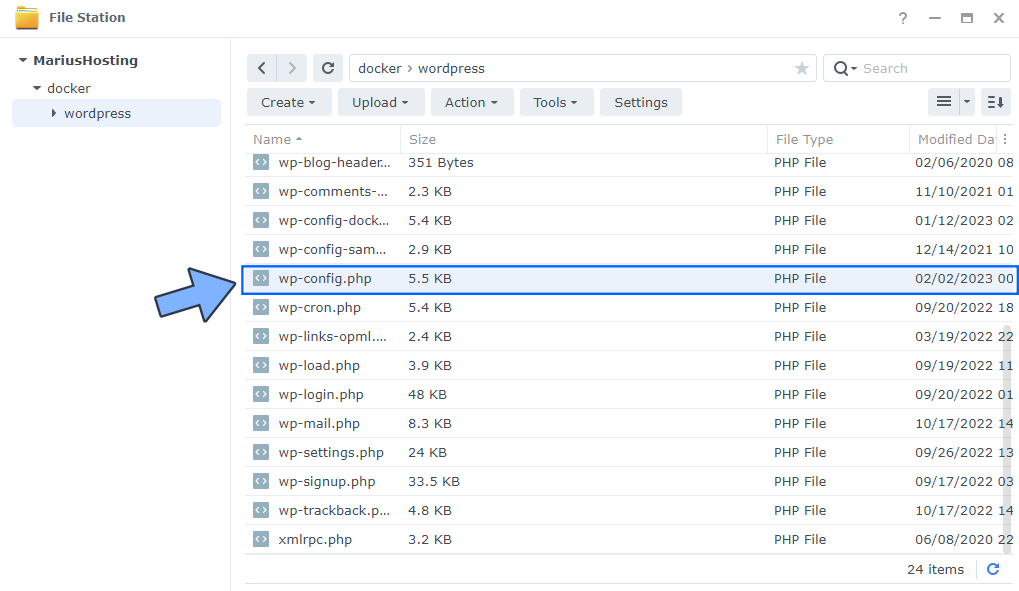
STEP 26
Under the WORDPRESS_DEBUG line, copy and paste these two supplementary lines below. Click X to save the file. Follow the instructions in the image below.
define('WP_REDIS_HOST', 'wordpress-redis');
define('WP_REDIS_PORT', '6379');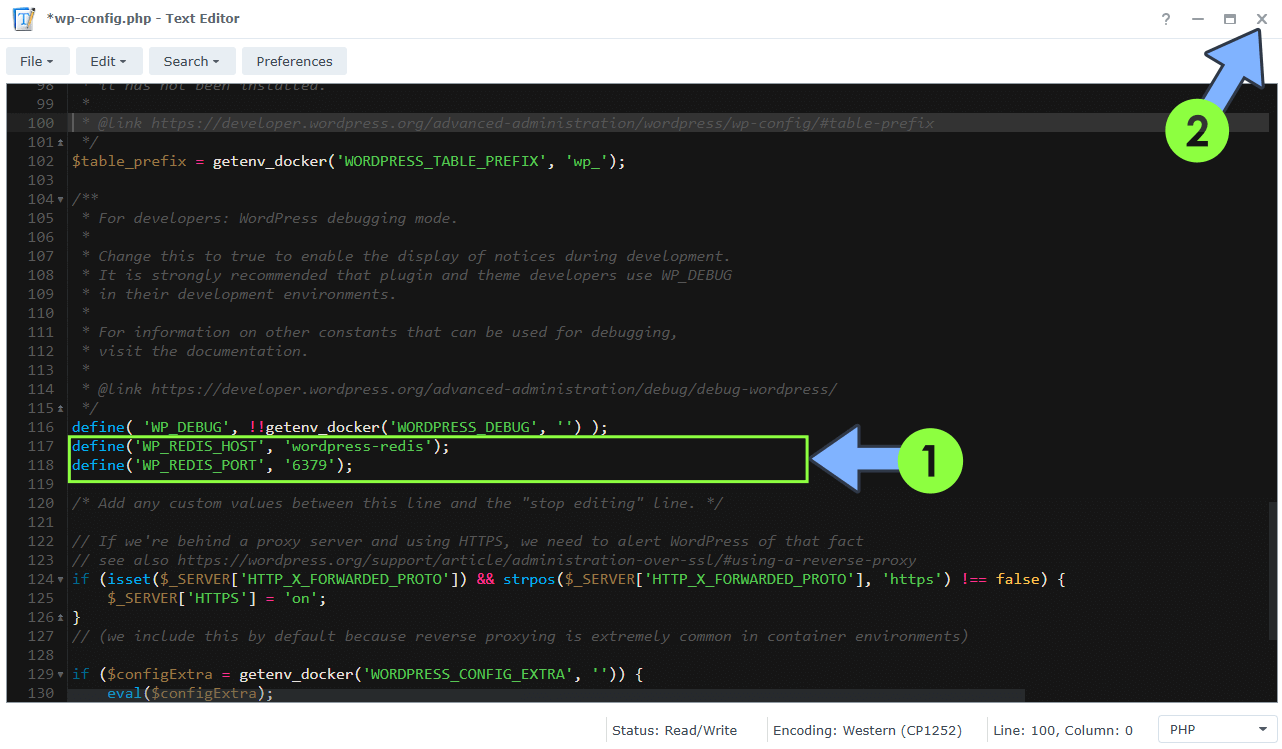
STEP 27
On the WordPress left sidebar, click on Plugins, then Add Plugin. Search for Redis Object Cache. When you find the plugin named Redis Object Cache, click Install Now then Activate it. Follow the instructions in the image below.
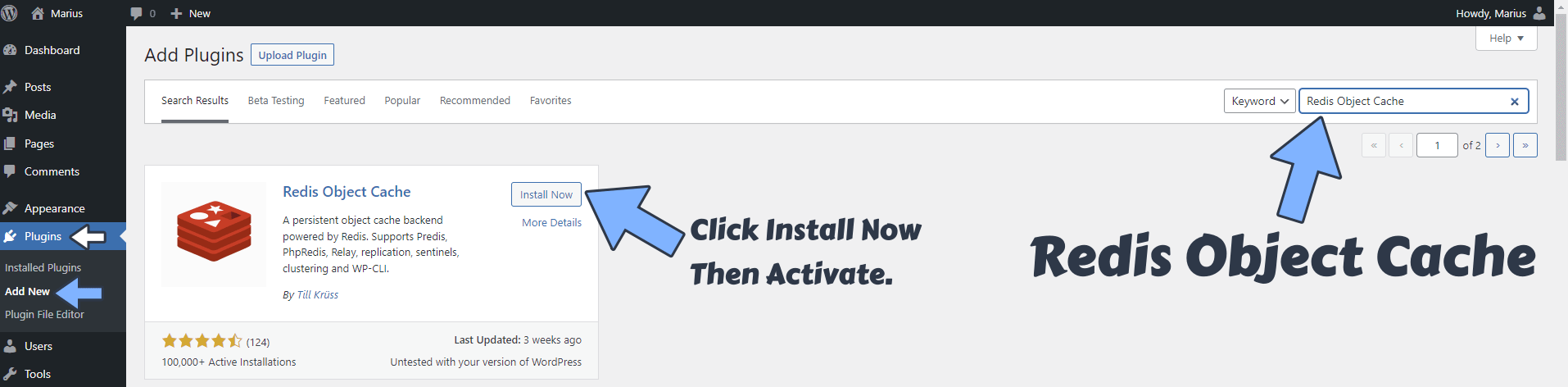
Note: WordPress uses the MySQL/MariaDB database to cache internal application objects like breadcrumbs, menu items etc. which are very heavy to generate. A database handles queries for page requests, and causes increased load-times when your website is loaded intensively. Redis provides a caching mechanism that acts as an alternative to your MySQL/MariaDB database. If someone is visiting your WordPress website, the MySQL/MariaDB queries required to generate the entire page are served via Redis which caches the results. This results in blazing fast load times, comparable to static pages without Redis. When a user requests a WordPress page for the first time, a MySQL/MariaDB database query is performed on your Synology NAS server. Redis will cache this query, so when another user requests the same identical WordPress page, the results are provided from Redis, without the need to query the MySQL/MariaDB database again. So, in a few words, if the query is not cached in Redis, the results are provided by your MySQL/MariaDB database, which are then added to the Redis cache. Redis stores data in memory rather than on an HDD or SSD cache; its response time is faster than others when performing read and write operations.
STEP 28
After the Redis Object Cache plugin is installed, you will find it under the Settings menu. Click on Redis. Click Enable Object Cache. Follow the instructions in the image below.
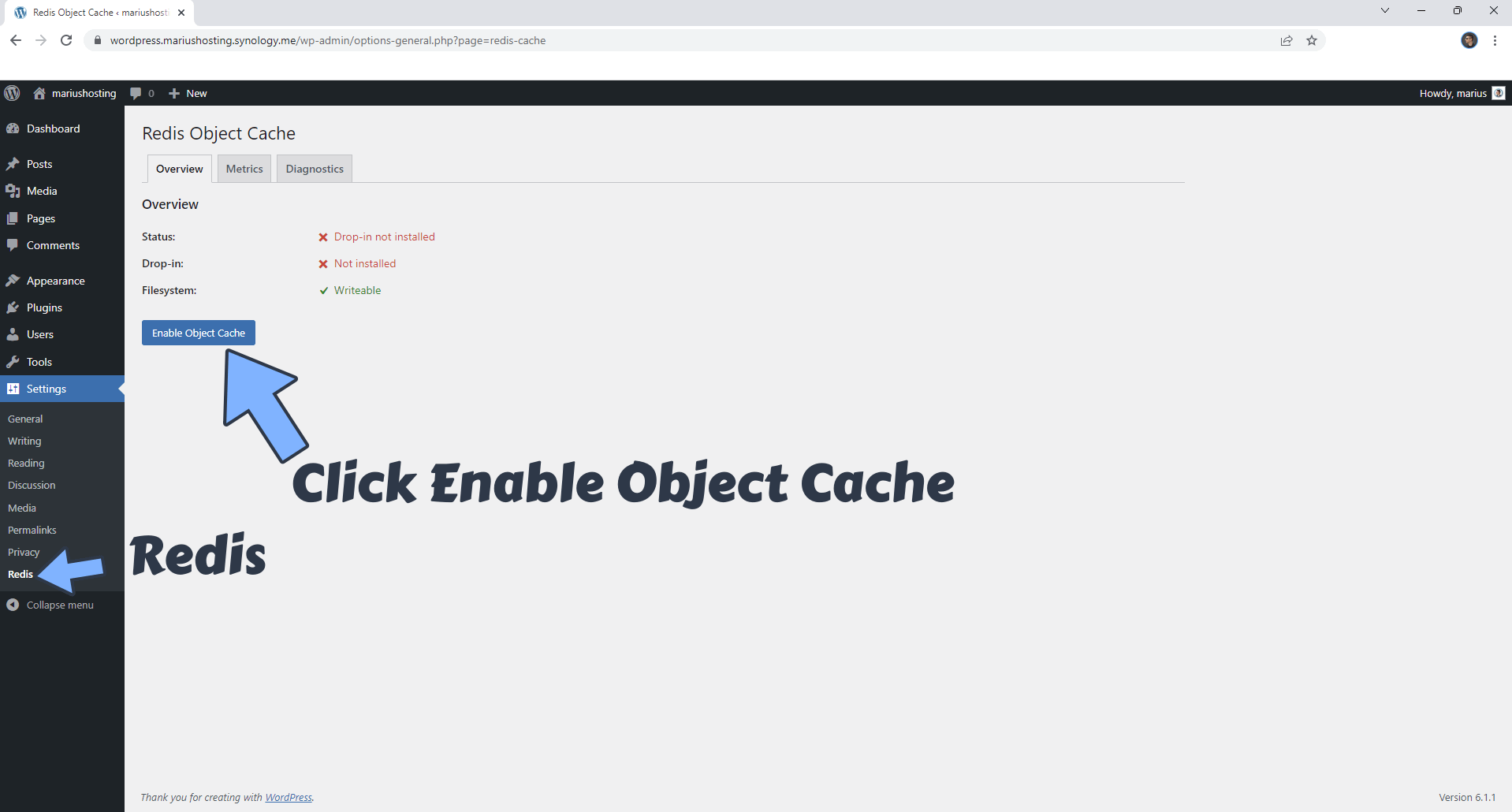
STEP 29
After you click Enable Object Cache, the Status will say Connected. Follow the instructions in the image below. ⚠️Warning: If you accidentally click Flush Cache, your Redis host will be disconnected. To solve this issue, just restart the WordPress-REDIS container via Portainer.
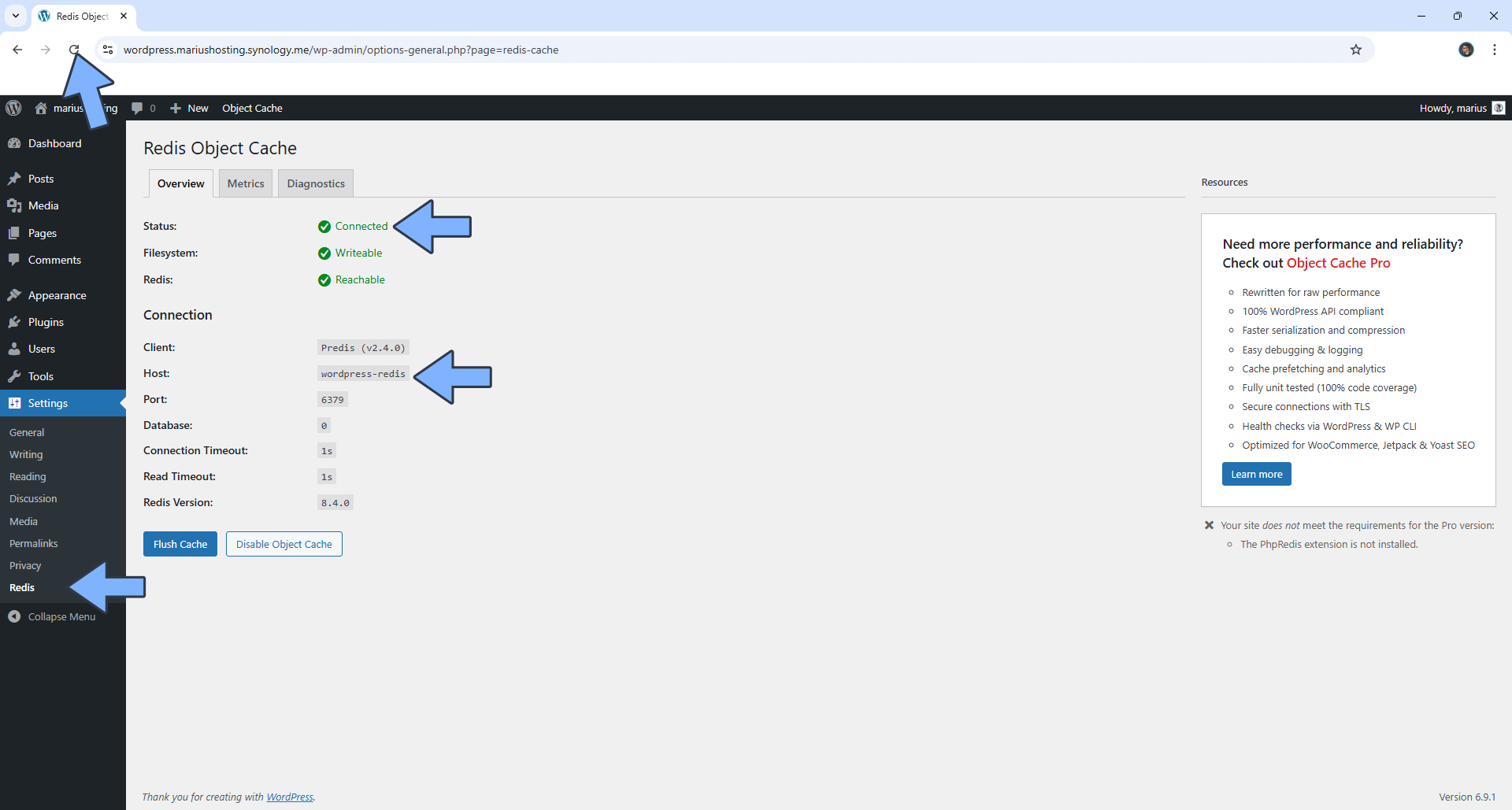
STEP 30
phpMyAdmin is the graphical interface for the MariaDB database. It will help you connect to your database. Open your browser and type in http://Synology-ip-address:2500 Connect to your MariaDB using root as Username and rootpass as Password. Click Log in. Follow the instructions in the image below.
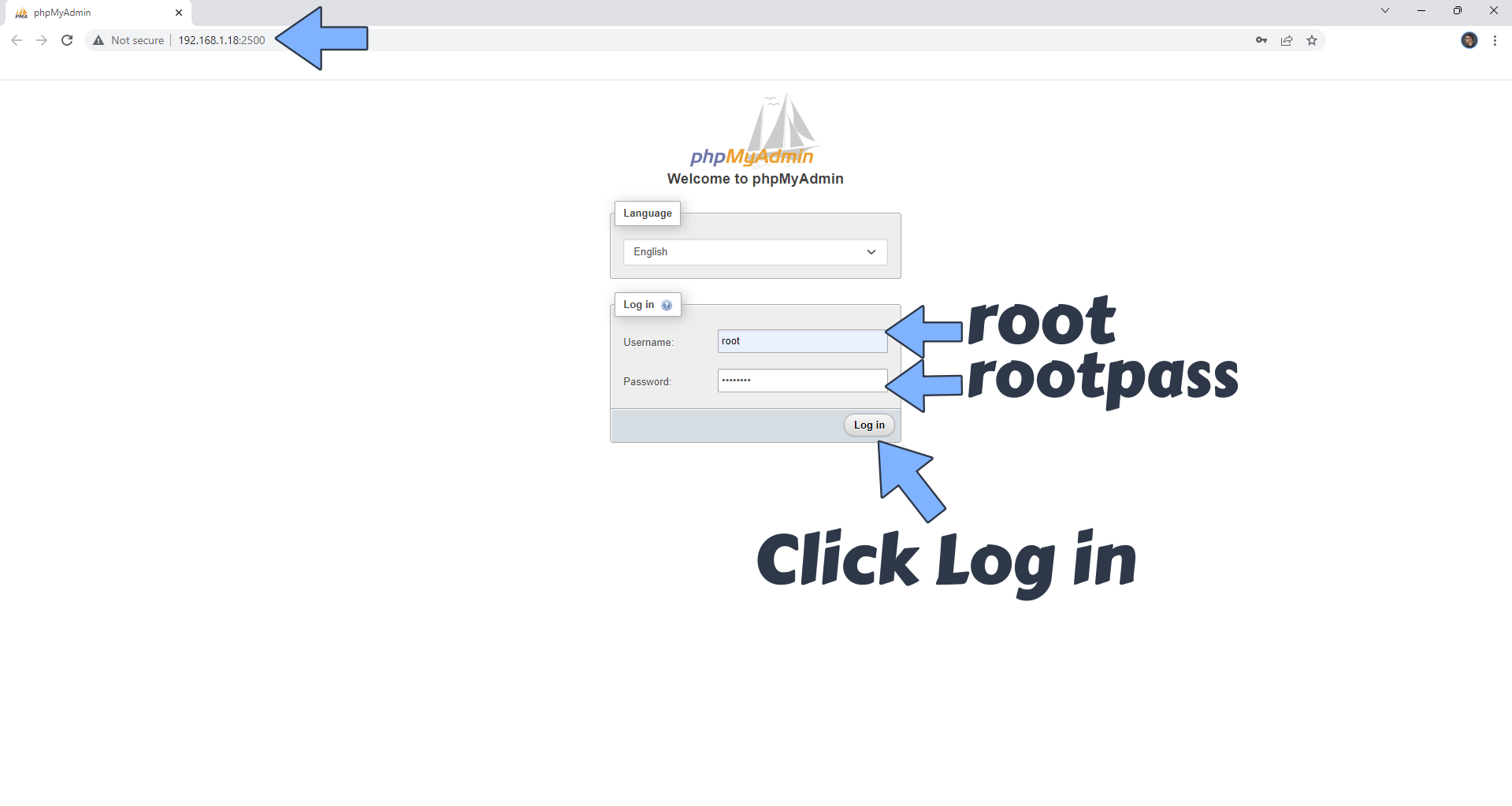
STEP 31
You can now download and back up your WordPress database without needing to install any backup plugin on your WordPress website. Warning: Do not expose the phpMyadmin instance to the Internet via Reverse Proxy. You can do it by using a strong password, but it’s not recommended to expose it. Keep it local.
Note: Find out how to backup your WordPress database using phpMyAdmin.
Note: Fix the error message: The phpMyAdmin configuration storage is not completely configured.
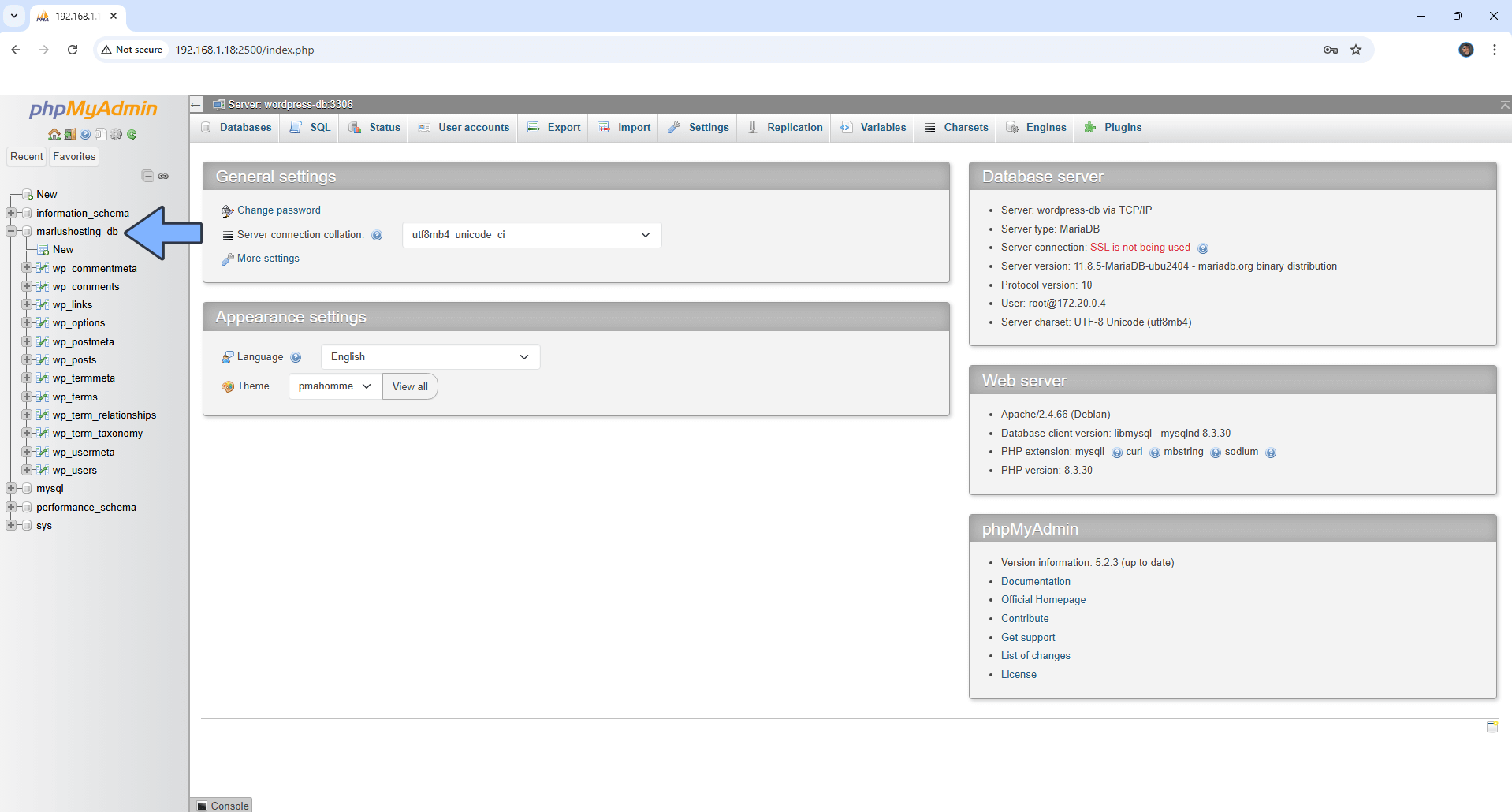
STEP 32
Find out how to add Email SMTP to your WordPress website so you can receive notifications via email.
STEP 33
Speed Up WordPress With Docker and Cron. Step by step guide on how to set up CRON in WordPress on your Synology NAS.
⚠️Note: If you encounter permission issues and not all containers are starting, ensure that your current NAS user has Read/Write permissions for the Docker folder in Control Panel > User & Group > Select the current NAS user > Edit tab > Permissions tab. You can also try to add Everyone read/write permission to the db and redis folders at STEP 12 like this other article from STEP 5 to STEP 9.
Enjoy WordPress!
Note: Can I run Docker on my Synology NAS? See the supported models.
Note: How to Back Up Docker Containers on your Synology NAS.
Note: Find out how to update the WordPress container with the latest image.
Note: How to Free Disk Space on Your NAS if You Run Docker.
Note: How to Schedule Start & Stop For Docker Containers.
Note: How to Activate Email Notifications.
Note: How to Add Access Control Profile on Your NAS.
Note: How to Change Docker Containers Restart Policy.
Note: How to Use Docker Containers With VPN.
Note: Convert Docker Run Into Docker Compose.
Note: How to Clean Docker.
Note: How to Clean Docker Automatically.
Note: Best Practices When Using Docker and DDNS.
Note: Some Docker Containers Need WebSocket.
Note: Find out the Best NAS Models For Docker.
Note: Activate Gmail SMTP For Docker Containers.
This post was updated on Thursday / February 5th, 2026 at 5:00 PM
