Semaphore UI is a modern open-source web interface and REST API for easily running, scheduling, and monitoring automation tasks. It offers a clean dashboard to execute Ansible playbooks, Terraform/OpenTofu/Terragrunt configurations, Bash scripts, and PowerShell scripts in a controlled way. Built as a lightweight self-hosted alternative to Ansible AWX/Tower, Rundeck, or Jenkins, it provides a simpler and more up-to-date experience with strong support for both Ansible and Terraform workflows. You can organize automation code, inventories, and credentials into projects, create reusable parameterized task templates, view full execution logs and history, set up cron-style schedules, pull code from Git repositories, manage variables and secrets securely, control access with user and team permissions, send failure notifications, and trigger jobs via a REST API for CI/CD integration. In this step by step guide I will show you how to install Semaphore UI on your Synology NAS using Docker and Portainer.
STEP 1
Please Support My work by Making a Donation.
STEP 2
Install Portainer using my step by step guide. If you already have Portainer installed on your Synology NAS, skip this STEP. Attention: Make sure you have installed the latest Portainer version.
STEP 3
Make sure you have a synology.me Wildcard Certificate. Follow my guide to get a Wildcard Certificate. If you already have a synology.me Wildcard certificate, skip this STEP.
STEP 4
Go to Control Panel / Login Portal / Advanced Tab / click Reverse Proxy. Follow the instructions in the image below.
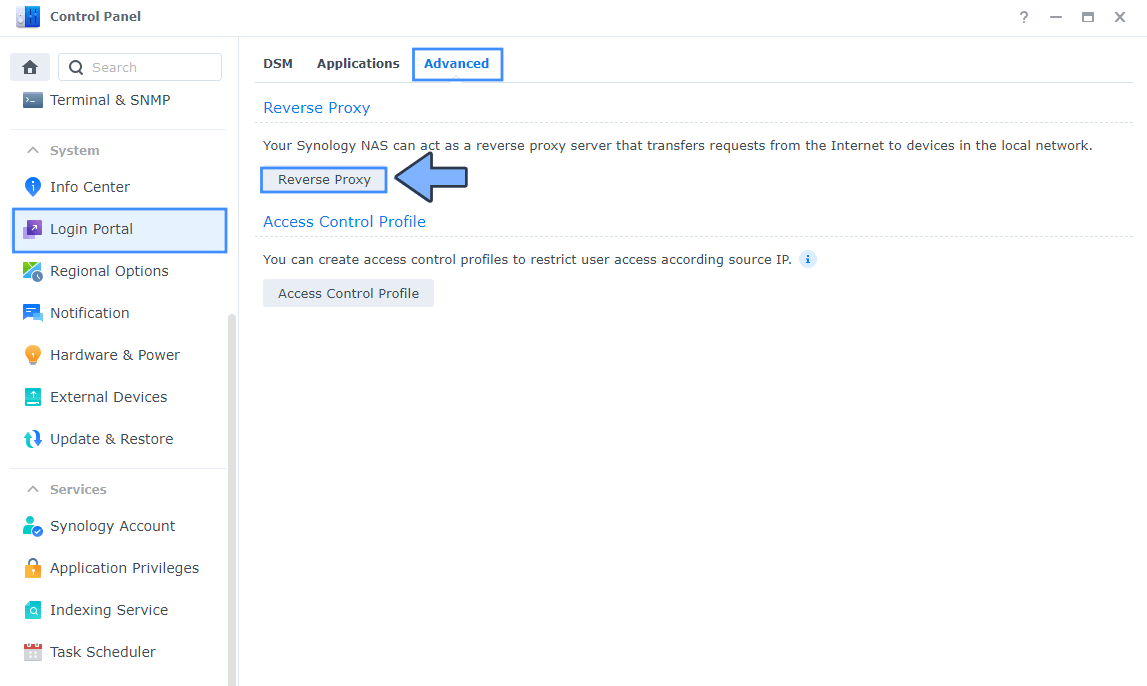
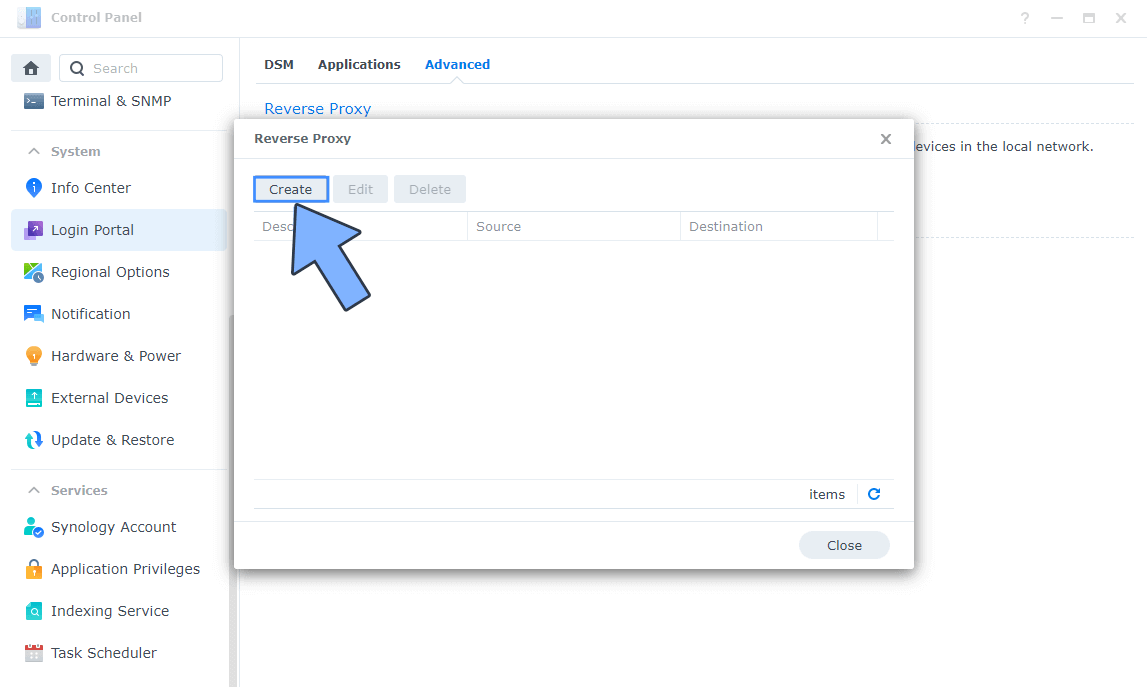
STEP 5
Now click the “Create” button. Follow the instructions in the image below.
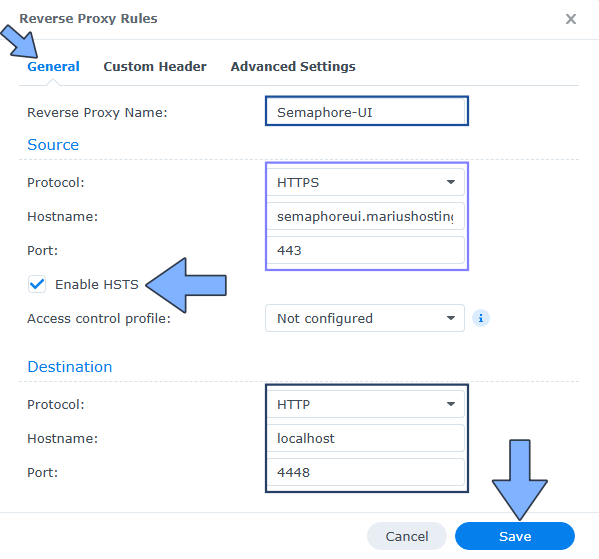
STEP 6
After you click the Create button, the window below will open. Follow the instructions in the image below.
On the General area, set the Reverse Proxy Name description: type in Semaphore-UI. After that, add the following instructions:
Source:
Protocol: HTTPS
Hostname: semaphoreui.yourname.synology.me
Port: 443
Check Enable HSTS
Destination:
Protocol: HTTP
Hostname: localhost
Port: 4448
STEP 7
On the Reverse Proxy Rules, click the Custom Header tab. Click Create and then, from the drop-down menu, click WebSocket. After you click on WebSocket, two Header Names and two Values will be automatically added. Click Save. Follow the instructions in the image below.
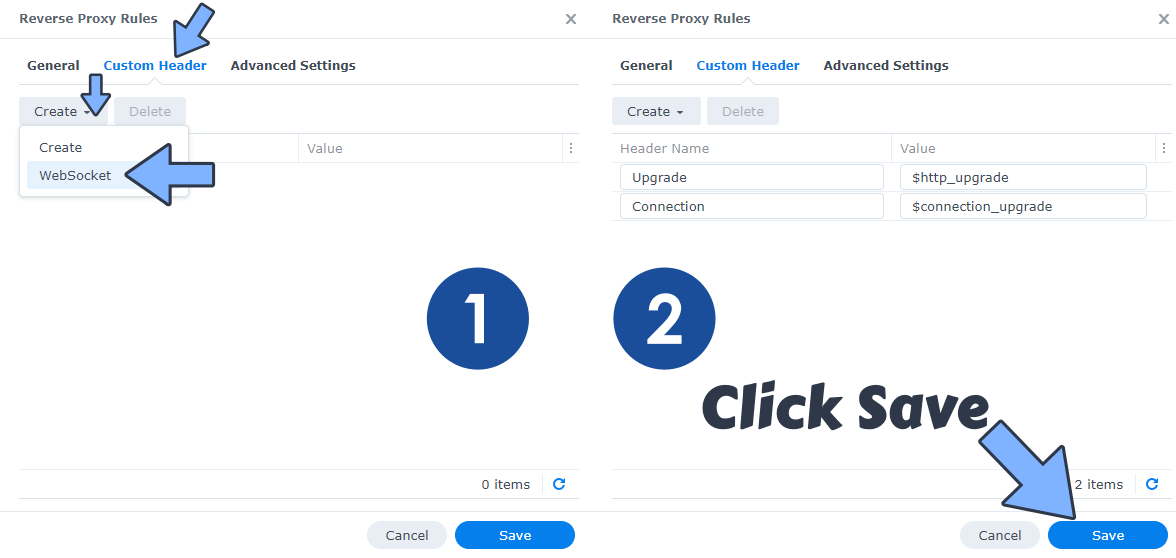
STEP 8
Go to Control Panel / Network / Connectivity tab/ Check Enable HTTP/2 then click Apply. Follow the instructions in the image below.
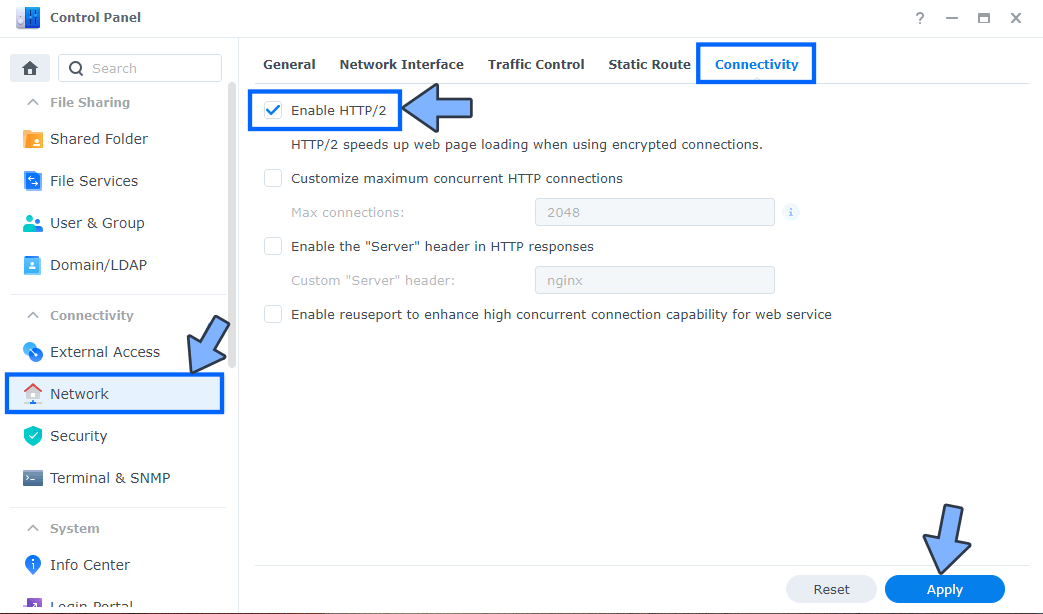
STEP 9
Go to Control Panel / Security / Advanced tab/ Check Enable HTTP Compression then click Apply. Follow the instructions in the image below.
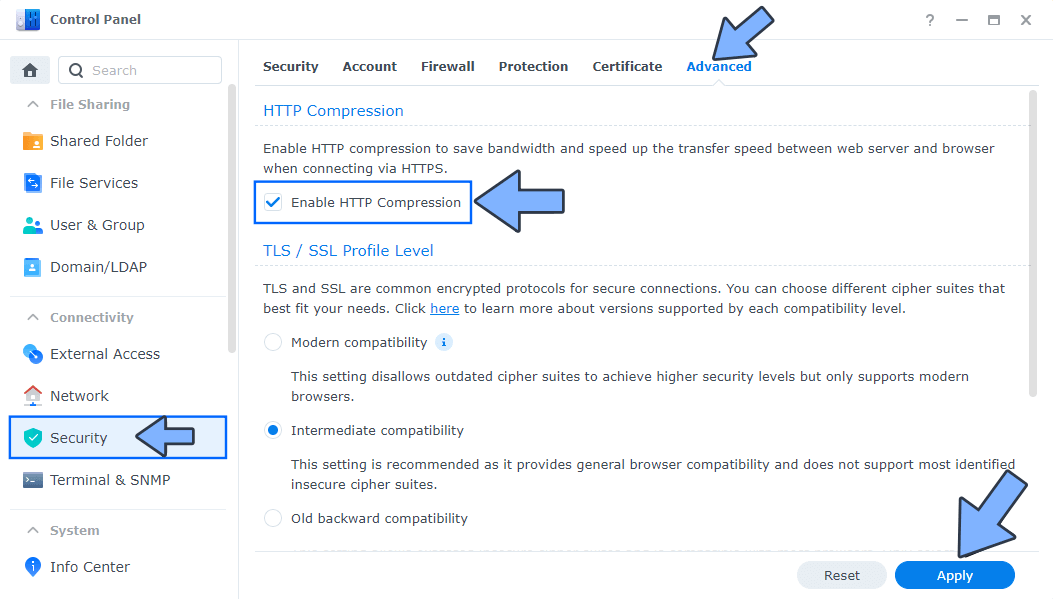
STEP 10
Go to File Station and open the docker folder. Inside the docker folder, create one new folder and name it semaphore. Follow the instructions in the image below.
Note: Be careful to enter only lowercase, not uppercase letters.
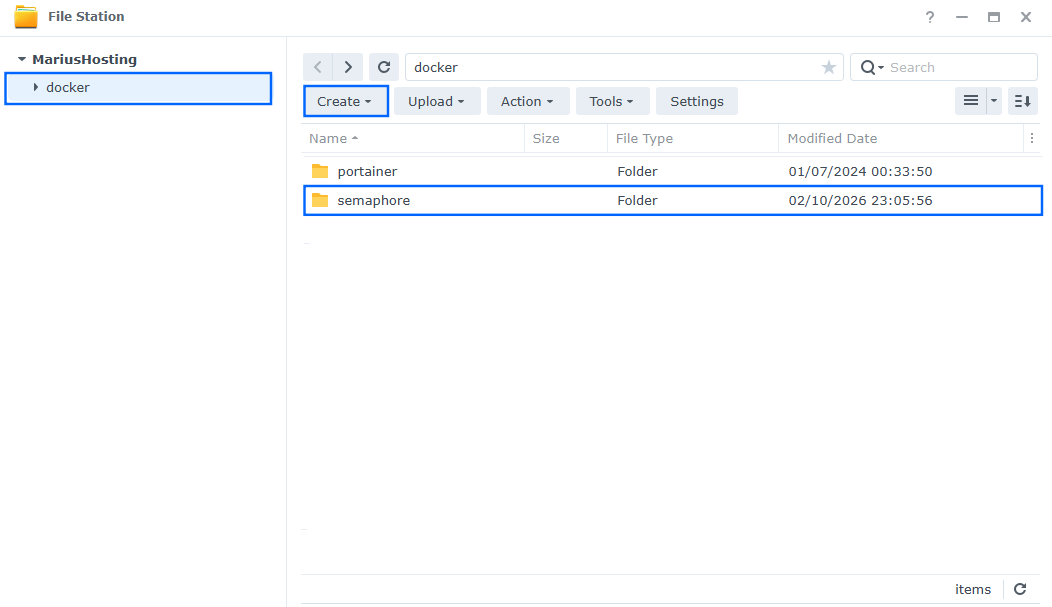
STEP 11
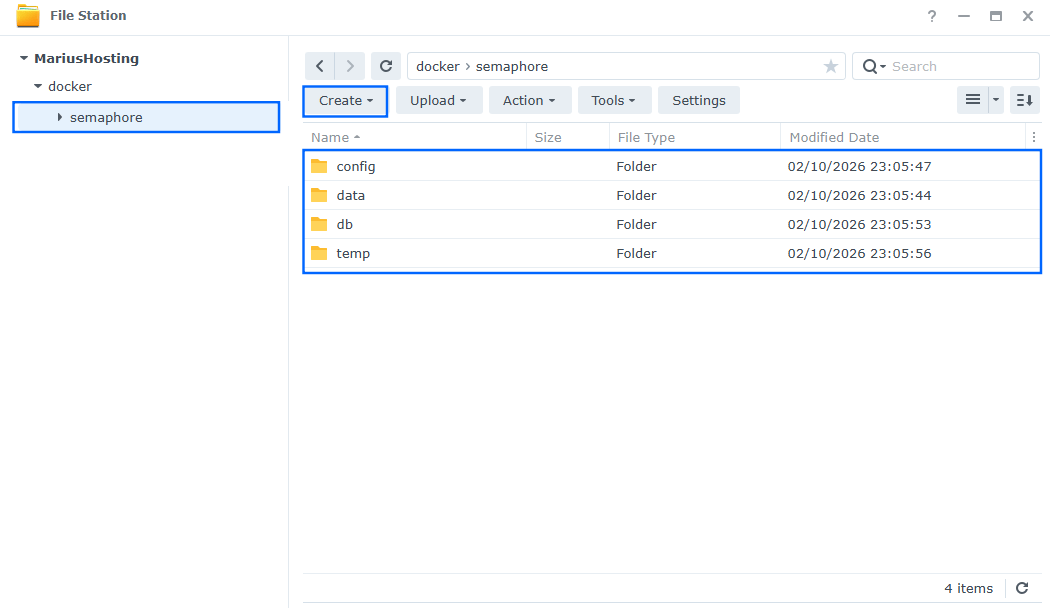
Now create four new folders inside the semaphore folder that you have previously created at STEP 10 and name them config, data, db, temp. Follow the instructions in the image below.
Note: Be careful to enter only lowercase, not uppercase letters.
STEP 12
Follow my step by step guide on how to activate SMTP for your Gmail account. This step is mandatory. Note: If you don’t want to use the easiest way for SMTP with Google and you already have SMTP details from your own Mail Server, you can just skip this STEP and use your personalized email SMTP details instead.
STEP 13
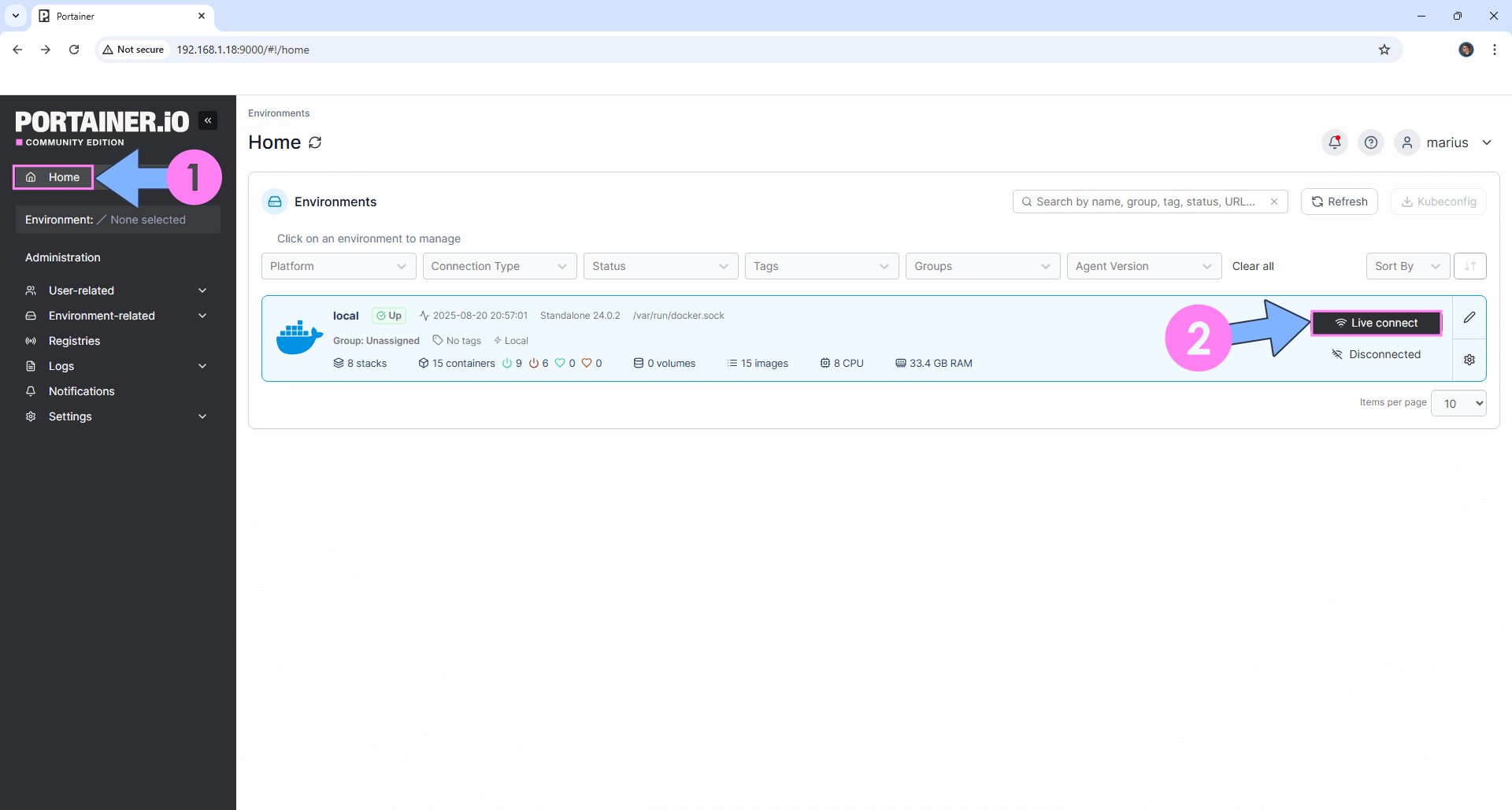
Log into Portainer using your username and password. On the left sidebar in Portainer, click on Home then Live connect. Follow the instructions in the image below.
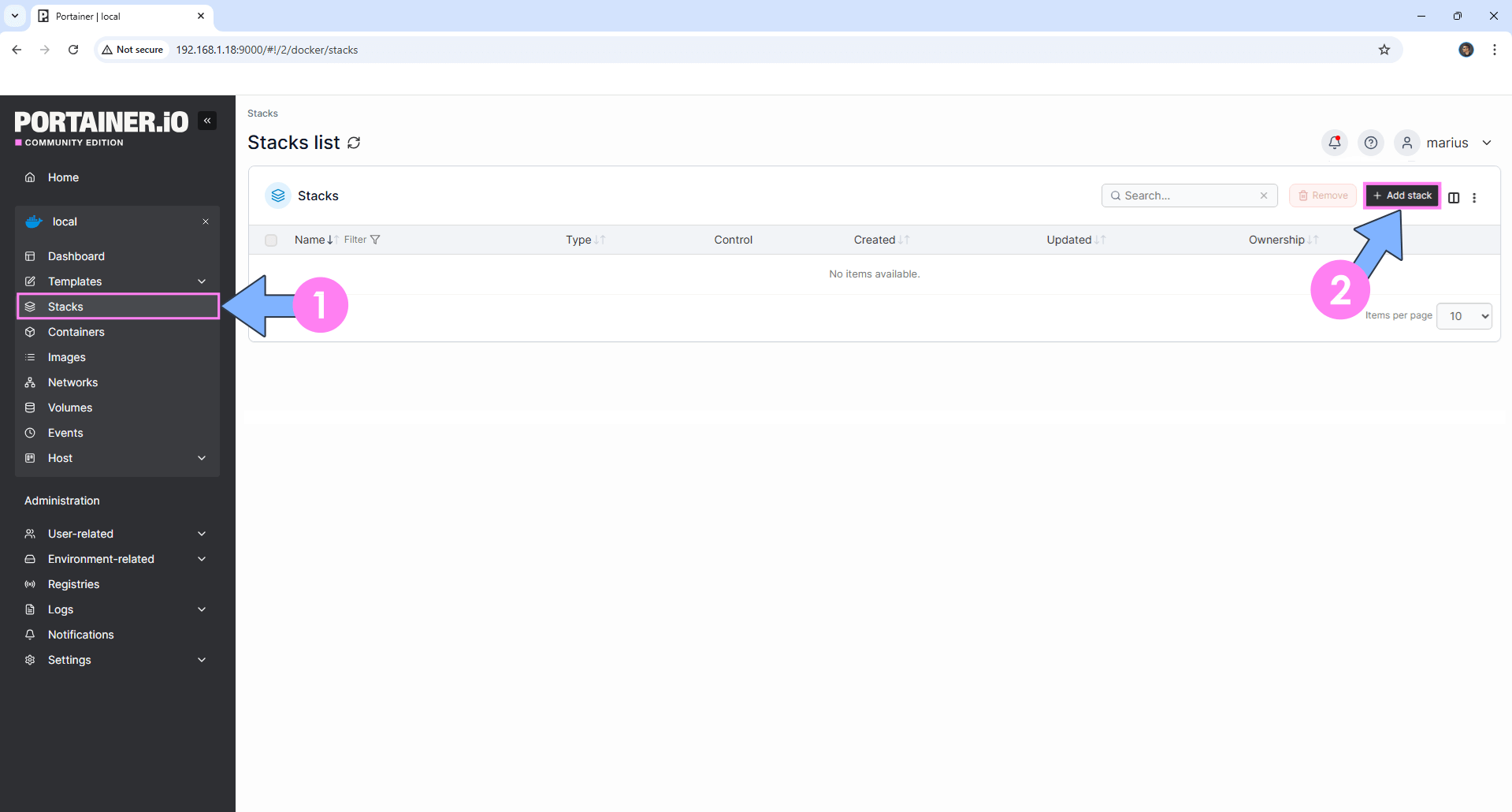
On the left sidebar in Portainer, click on Stacks then + Add stack. Follow the instructions in the image below.
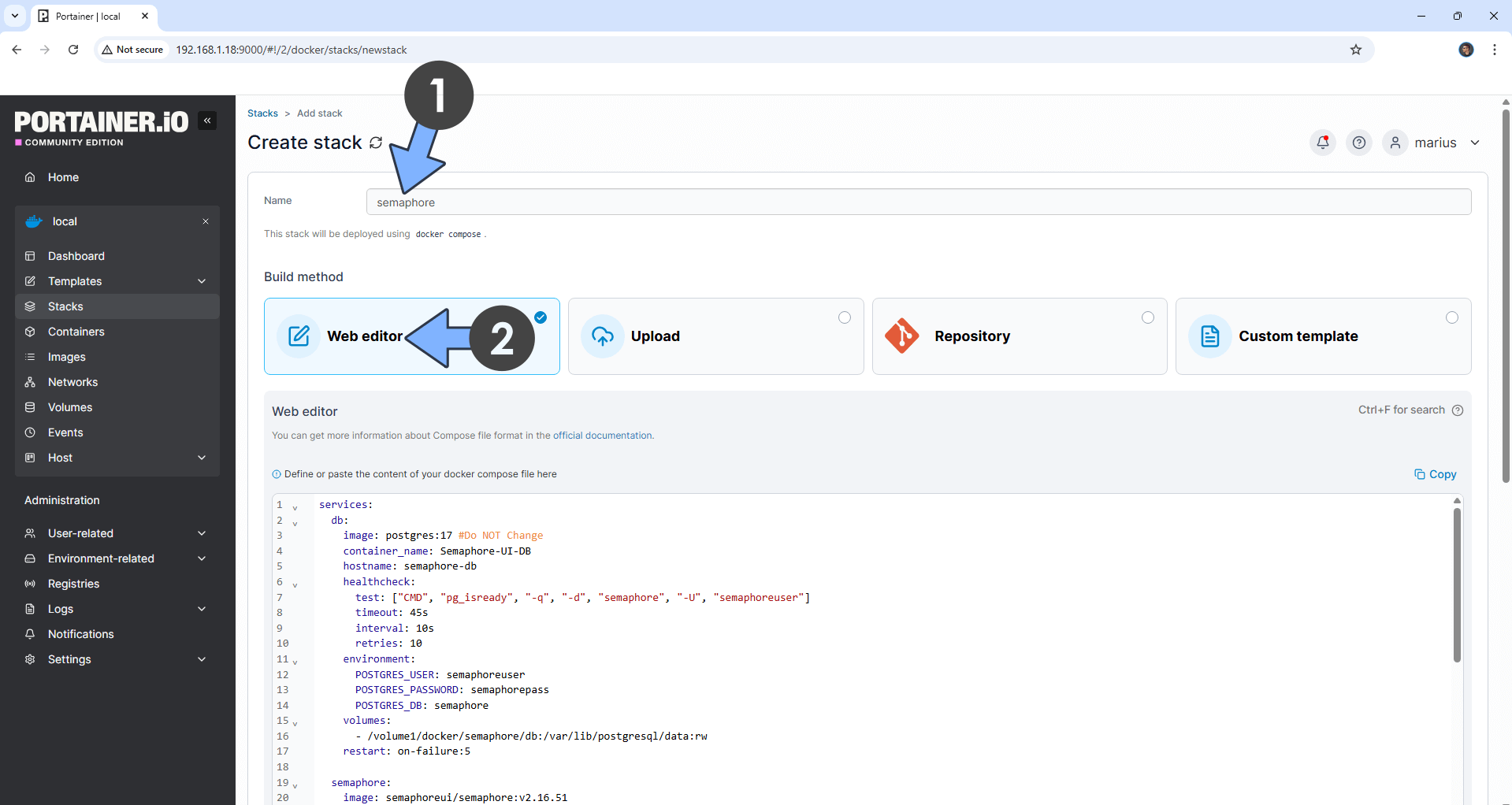
STEP 14
In the Name field type in semaphore. Follow the instructions in the image below.
services:
db:
image: postgres:17 #Do NOT Change
container_name: Semaphore-UI-DB
hostname: semaphore-db
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD", "pg_isready", "-q", "-d", "semaphore", "-U", "semaphoreuser"]
timeout: 45s
interval: 10s
retries: 10
environment:
POSTGRES_USER: semaphoreuser
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: semaphorepass
POSTGRES_DB: semaphore
volumes:
- /volume1/docker/semaphore/db:/var/lib/postgresql/data:rw
restart: on-failure:5
semaphore:
image: semaphoreui/semaphore:v2.16.51
container_name: Semaphore-UI
user: 0:0
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD-SHELL", "nc -z 127.0.0.1 3000 || exit 1"]
interval: 10s
timeout: 5s
retries: 3
start_period: 90s
ports:
- 4448:3000
environment:
SEMAPHORE_WEB_ROOT: https://semaphoreui.yourname.synology.me
SEMAPHORE_DB_DIALECT: postgres
SEMAPHORE_DB_HOST: semaphore-db
SEMAPHORE_DB_NAME: semaphore
SEMAPHORE_DB_USER: semaphoreuser
SEMAPHORE_DB_PASS: semaphorepass
SEMAPHORE_ADMIN: marius
SEMAPHORE_ADMIN_PASSWORD: mariushosting
SEMAPHORE_ADMIN_NAME: Lixandru Marius Bogdan
SEMAPHORE_ADMIN_EMAIL: yourown@email
SEMAPHORE_USE_REMOTE_RUNNER: "True"
SEMAPHORE_RUNNER_REGISTRATION_TOKEN: dOxZYTTZgXKMHkqLBIQVImayQXAVWdzGBPuFJKggzcgvgPJPXpWzqzKaUOIOGGIr
SEMAPHORE_EMAIL_HOST: smtp.gmail.com
SEMAPHORE_EMAIL_ALERT: True
SEMAPHORE_EMAIL_TLS: True
SEMAPHORE_EMAIL_PORT: 465
SEMAPHORE_EMAIL_SENDER: Your-own-gmail-address
SEMAPHORE_EMAIL_USERNAME: Your-own-gmail-address
SEMAPHORE_EMAIL_PASSWORD: Your-own-app-password
SEMAPHORE_EMAIL_SECURE: true
ANSIBLE_HOST_KEY_CHECKING: "False"
SEMAPHORE_DB_OPTIONS: '{"sslmode":"disable"}'
volumes:
- /volume1/docker/semaphore/data:/var/lib/semaphore:rw
- /volume1/docker/semaphore/config:/etc/semaphore:rw
- /volume1/docker/semaphore/temp:/tmp/semaphore:rw
depends_on:
db:
condition: service_healthy
restart: on-failure:5
Note: Before you paste the code above in the Web editor area below, change the value for SEMAPHORE_WEB_ROOT and type in your own synology.me DDNS with https:// at the beginning that you have previously created at STEP 6.
Note: Before you paste the code above in the Web editor area below, change the value for SEMAPHORE_ADMIN. marius is an example for an admin username. You should add your own admin username. You will need this Username later at STEP 18.
Note: Before you paste the code above in the Web editor area below, change the value for SEMAPHORE_ADMIN_PASSWORD. mariushosting is an example for an admin password. You should add your own admin password. You will need this Password later at STEP 18.
Note: Before you paste the code above in the Web editor area below, change the value for SEMAPHORE_ADMIN_NAME. Type in your own Name.
Note: Before you paste the code above in the Web editor area below, change the value for SEMAPHORE_ADMIN_EMAIL. Type in your own Email Address.
Note: Before you paste the code above in the Web editor area below, change the value for SEMAPHORE_RUNNER_REGISTRATION_TOKEN. (Generate your own Random 64 length REGISTRATION_TOKEN.)
Note: Before you paste the code above in the Web editor area below, change the value for SEMAPHORE_EMAIL_SENDER and type in your own Gmail address. STEP 12.
Note: Before you paste the code above in the Web editor area below, change the value for SEMAPHORE_EMAIL_USERNAME and type in your own Gmail address. STEP 12.
Note: Before you paste the code above in the Web editor area below, change the value for SEMAPHORE_EMAIL_PASSWORD and type in your own Gmail app password. STEP 12. ⚠️Warning: Do NOT confuse with your own Gmail password. This is the Gmail APP password.
STEP 15
Scroll down on the page until you see a button called Deploy the stack. Click on it. Follow the instructions in the image below. The installation process can take up to a few minutes. It will depend on your Internet speed connection.
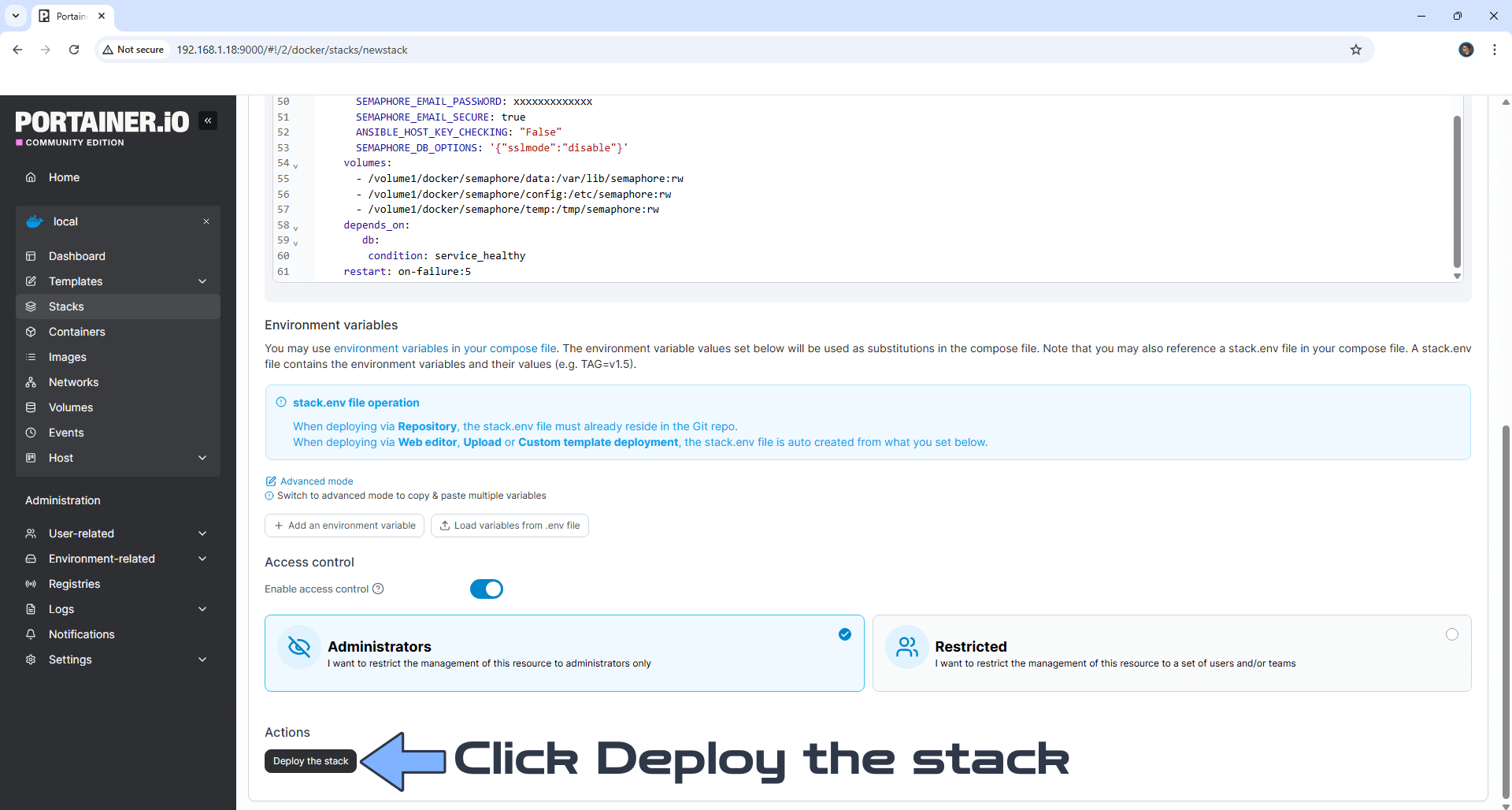
STEP 16
If everything goes right, you will see this message at the top right of your screen: “Success Stack successfully deployed“.
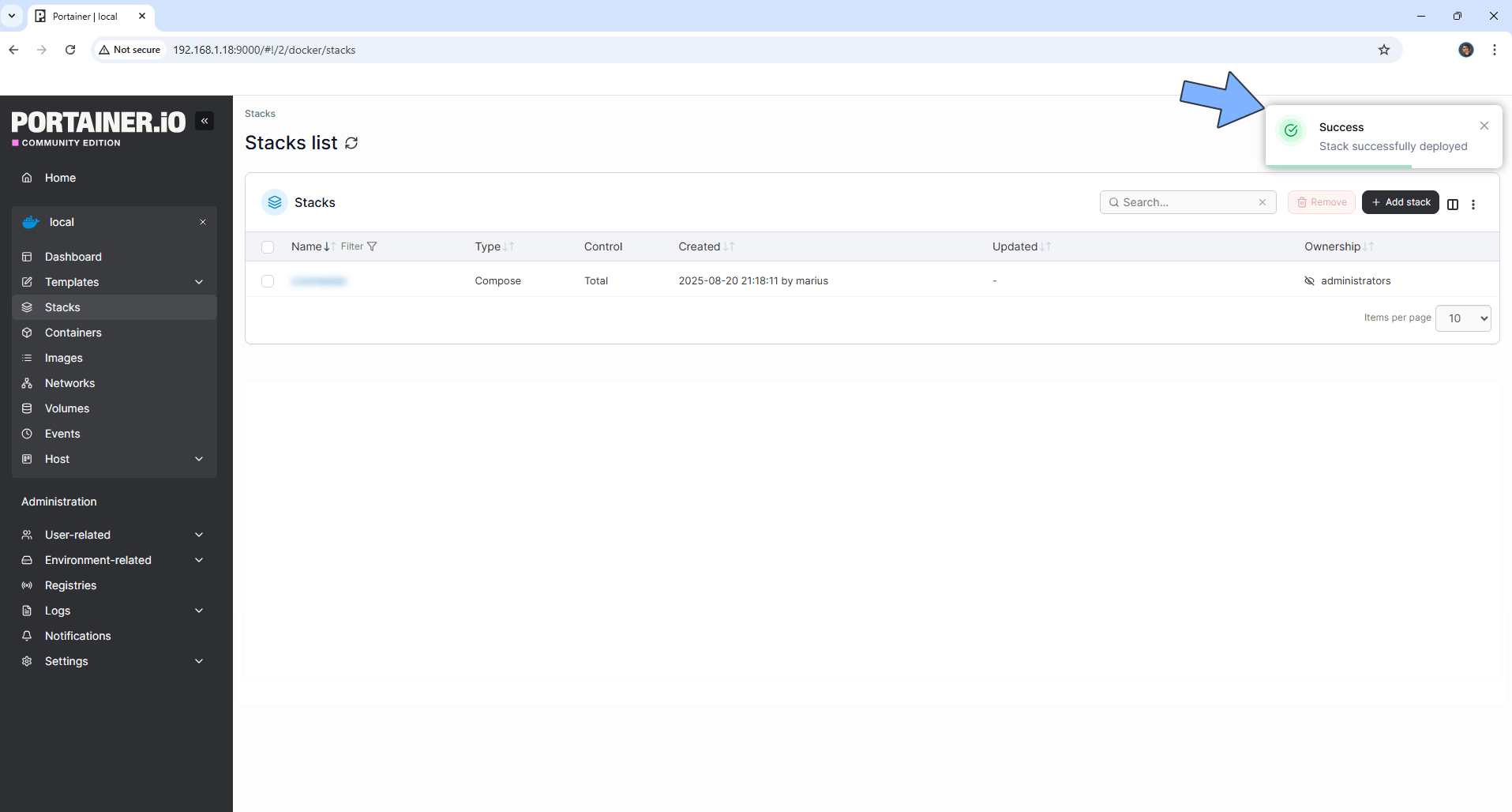
STEP 17
🟢Please Support My work by Making a Donation. Almost 99,9% of the people that install something using my guides forget to support my work, or just ignore STEP 1. I’ve been very honest about this aspect of my work since the beginning: I don’t run any ADS, I don’t require subscriptions, paid or otherwise, I don’t collect IPs, emails, and I don’t have any referral links from Amazon or other merchants. I also don’t have any POP-UPs or COOKIES. I have repeatedly been told over the years how much I have contributed to the community. It’s something I love doing and have been honest about my passion since the beginning. But I also Need The Community to Support me Back to be able to continue doing this work.
STEP 18
Now open your browser and type in your HTTPS/SSL certificate like this https://semaphoreui.yourname.synology.me that you have previously created at STEP 6. In my case it’s https://semaphoreui.mariushosting.synology.me If everything goes right, you will see the Semaphore UI login page. Type in your own Username (SEMAPHORE_ADMIN) and Password (SEMAPHORE_ADMIN_PASSWORD) that you have previously created at STEP 14. Click SIGN IN. Follow the instructions in the image below.
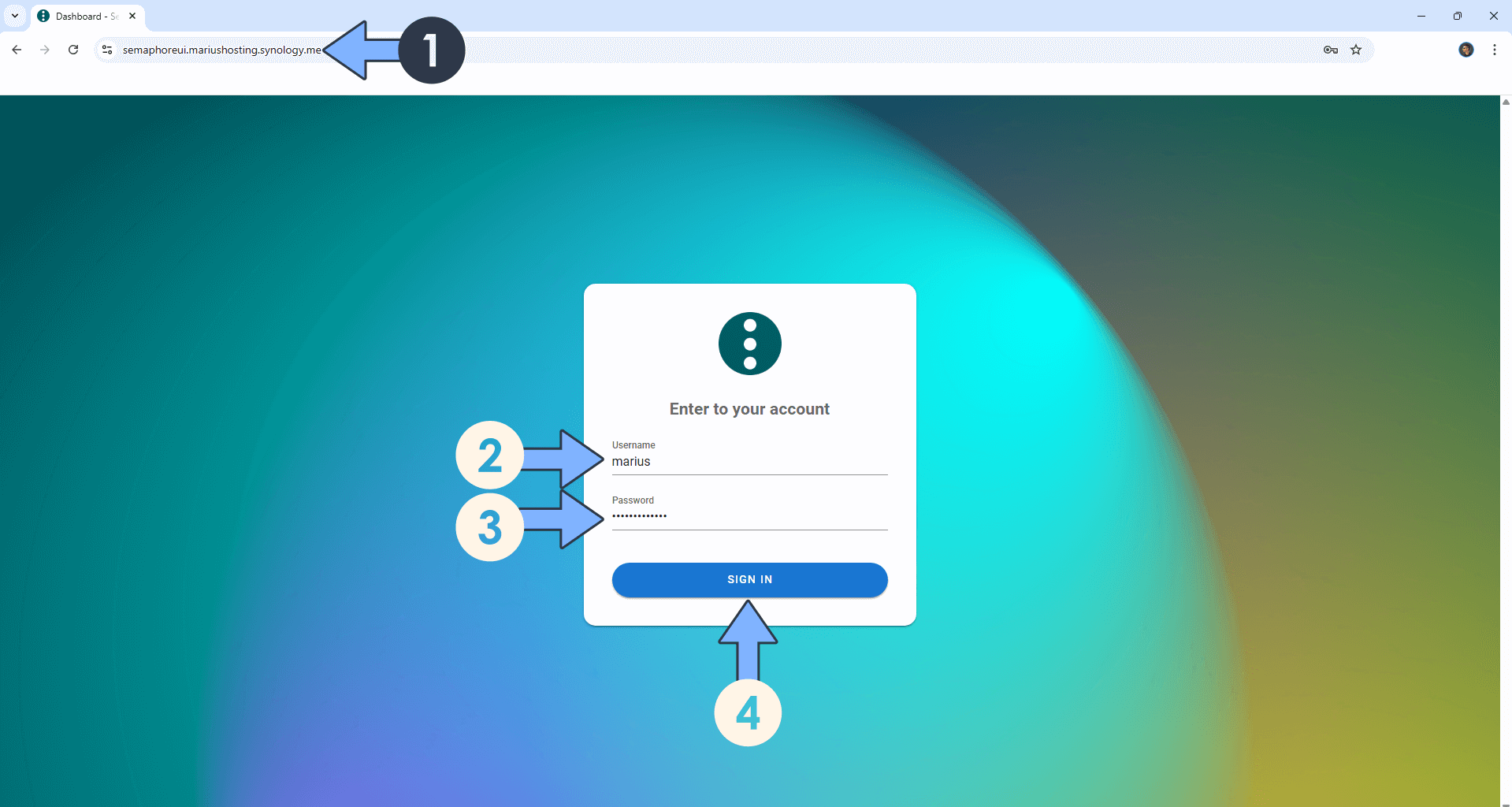
STEP 19
Create your first project! Follow the instructions in the image below.
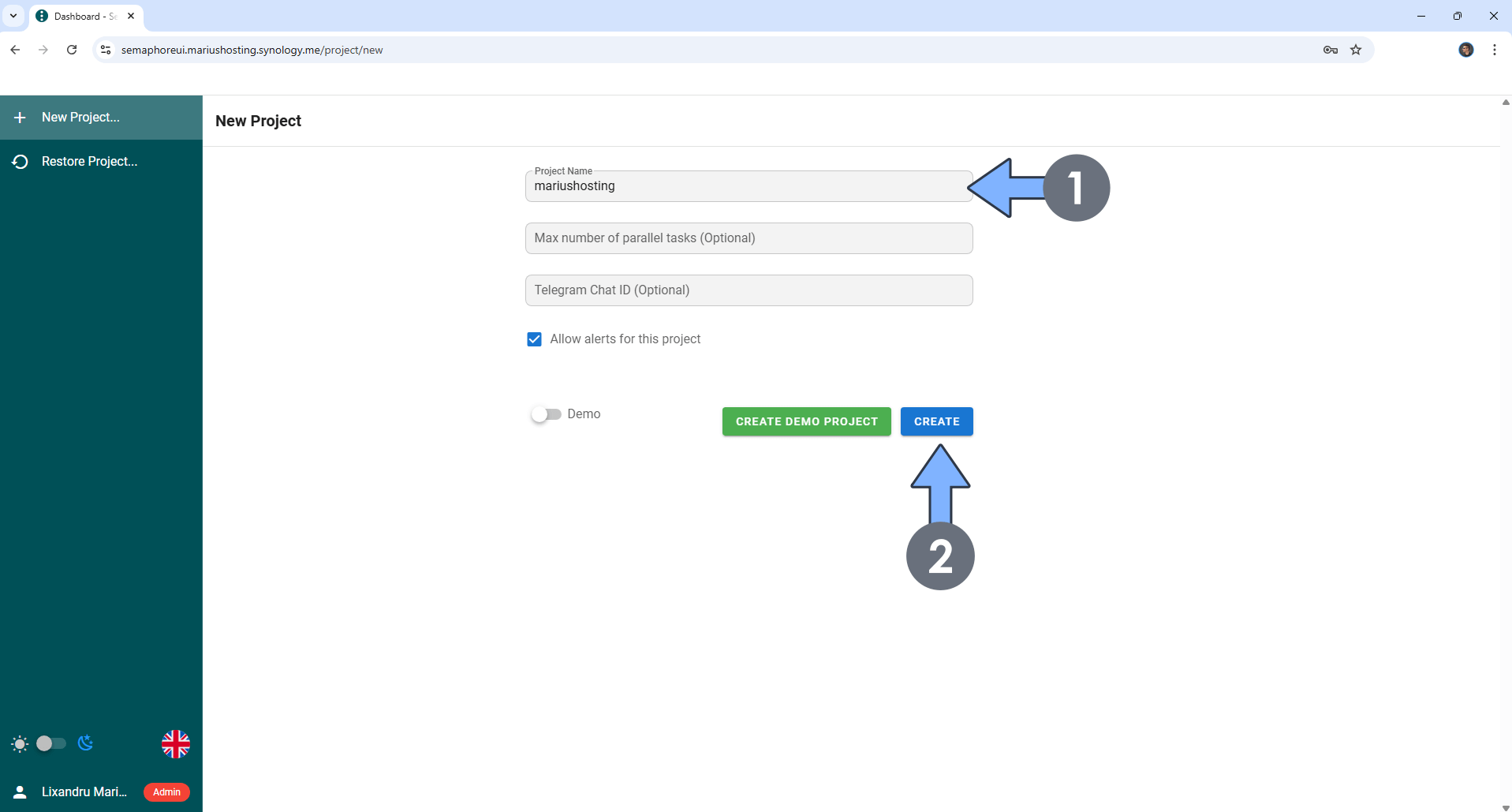
STEP 20
Your Semaphore UI dashboard at a glance!
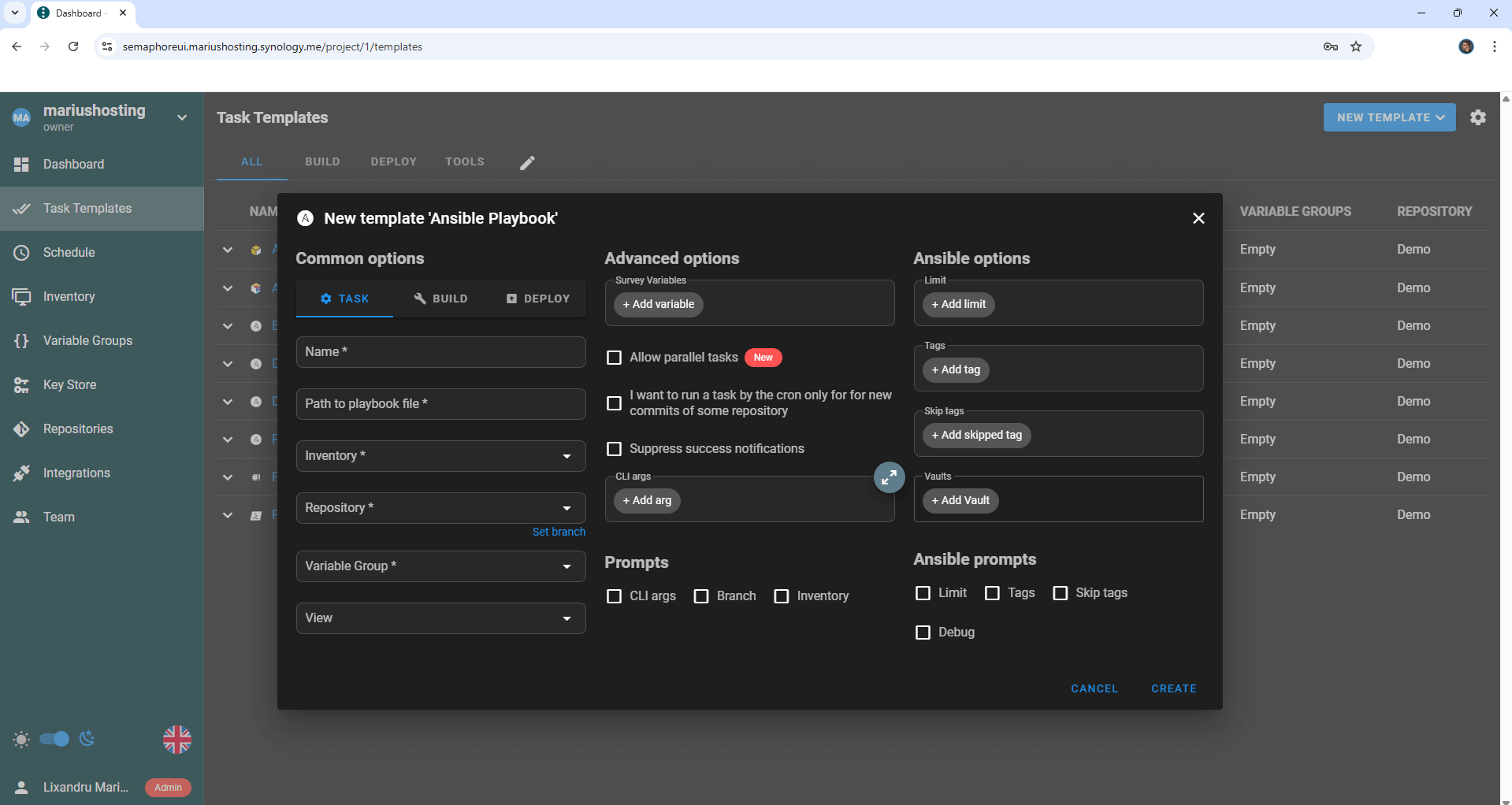
Enjoy Semaphore UI!
If you encounter issues by using this container, make sure to check out the Common Docker issues article.
Note: Can I run Docker on my Synology NAS? See the supported models.
Note: How to Back Up Docker Containers on your Synology NAS.
Note: Find out how to update the Semaphore UI container with the latest image.
Note: How to Free Disk Space on Your NAS if You Run Docker.
Note: How to Schedule Start & Stop For Docker Containers.
Note: How to Activate Email Notifications.
Note: How to Add Access Control Profile on Your NAS.
Note: How to Change Docker Containers Restart Policy.
Note: How to Use Docker Containers With VPN.
Note: Convert Docker Run Into Docker Compose.
Note: How to Clean Docker.
Note: How to Clean Docker Automatically.
Note: Best Practices When Using Docker and DDNS.
Note: Some Docker Containers Need WebSocket.
Note: Find out the Best NAS Models For Docker.
Note: Activate Gmail SMTP For Docker Containers.
This post was updated on Monday / March 2nd, 2026 at 1:51 PM
