
PostgreSQL, also known as Postgres, is a free and open-source relational database management system emphasizing extensibility and SQL compliance. It was originally named POSTGRES, referring to its origins as a successor to the Ingres database developed at the University of California, Berkeley. In this guide yow will also be installing pgAdmin, a web-based Graphical User Interface (GUI) management application used to communicate with PostgreSQL and derivative relational databases on both local and remote servers. In this step by step guide I will show you how to install PostgreSQL on your Synology NAS using Docker & Portainer.
STEP 1
Please Support My work by Making a Donation.
STEP 2
Install Portainer using my step by step guide. If you already have Portainer installed on your Synology NAS, skip this STEP. Attention: Make sure you have installed the latest Portainer version.
STEP 3
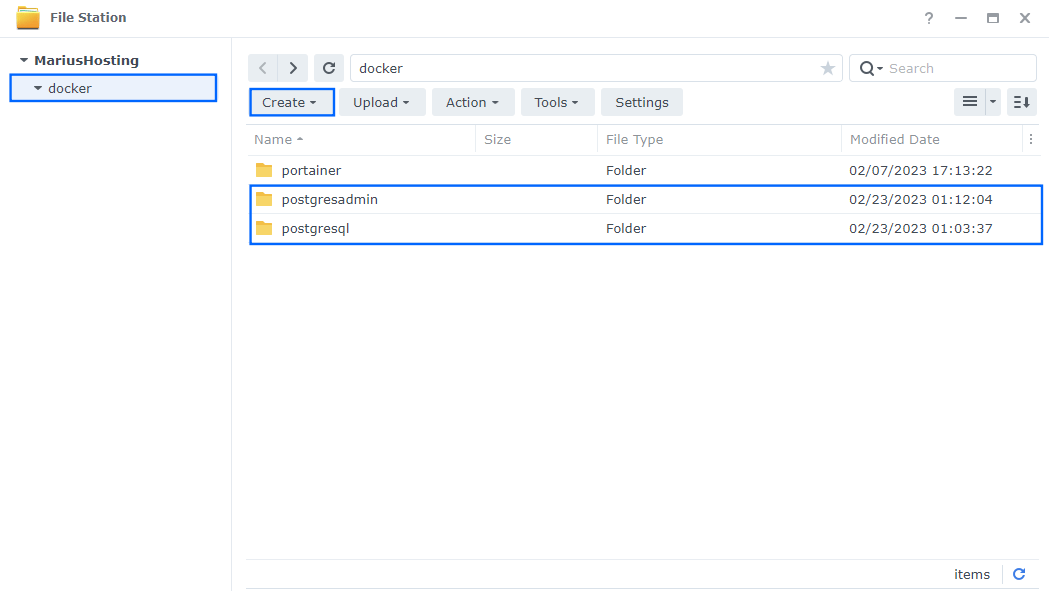
Go to File Station and open the docker folder. Inside the docker folder, create two new folder and name them postgresadmin and postgresql. Follow the instructions in the image below.
Note: Be careful to enter only lowercase, not uppercase letters.
STEP 4
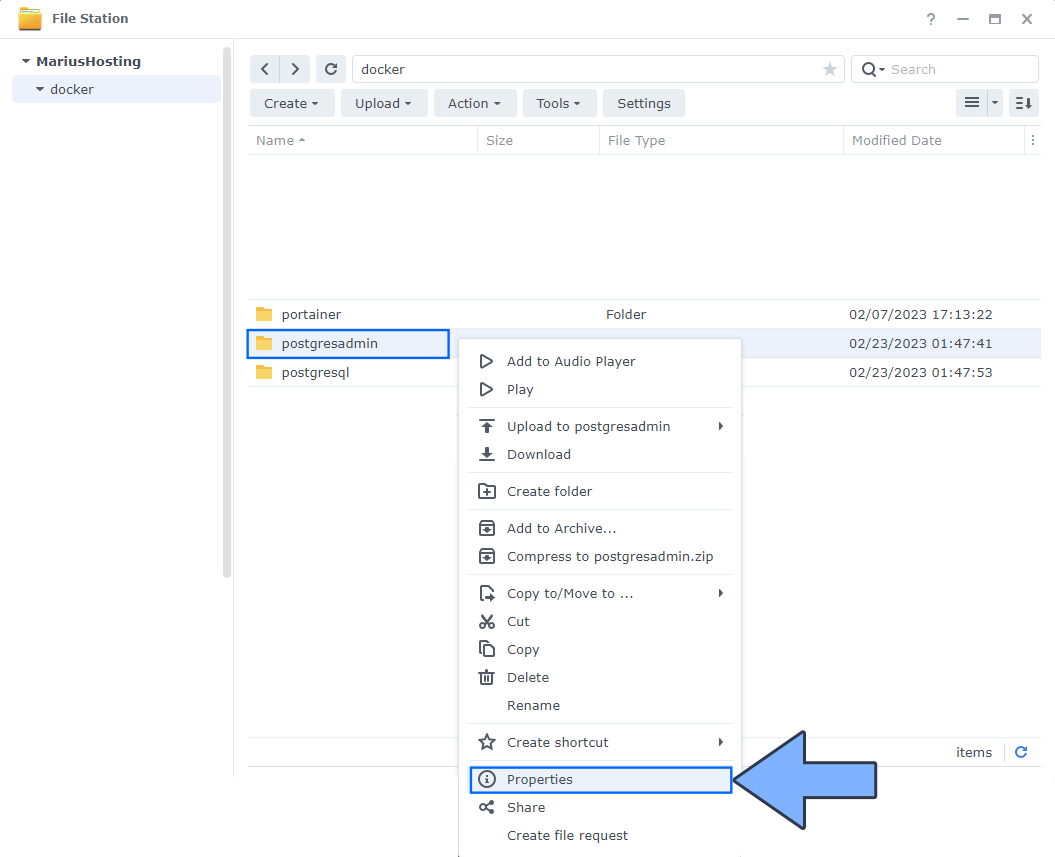
Right click on the postgresadmin folder that you have previously created at STEP 3 then click Properties. Follow the instructions in the image below.
STEP 5
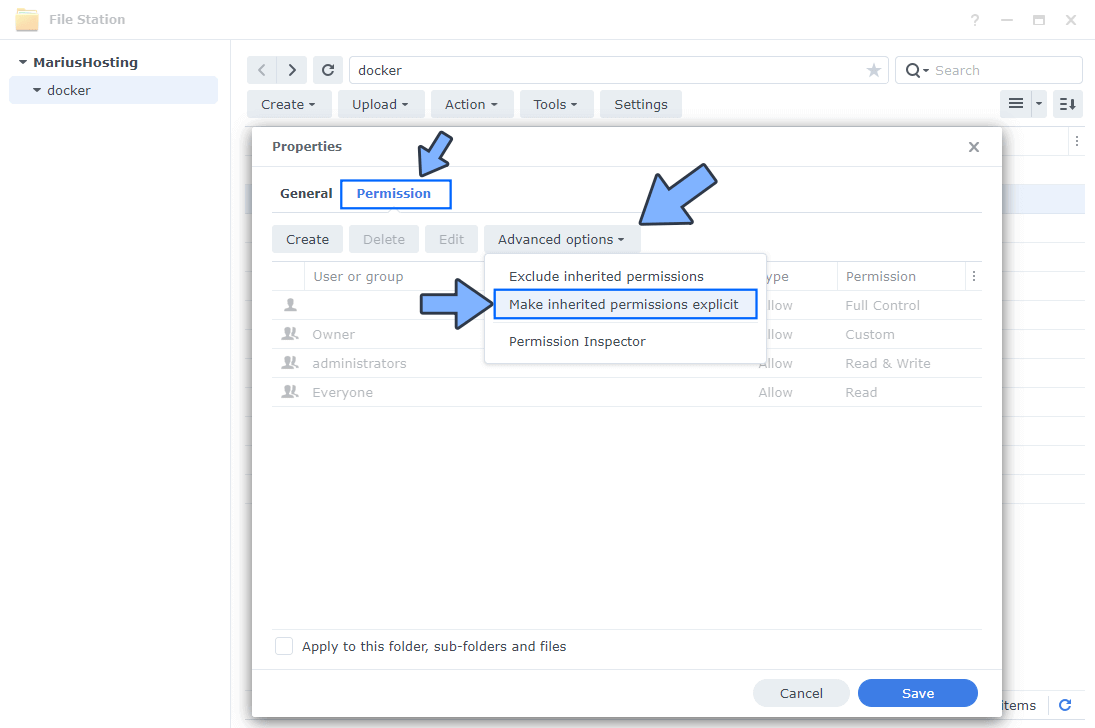
Go to the Permission tab then click Advanced options. From the drop-down menu choose “Make inherited permissions explicit“. Follow the instructions in the image below.
STEP 6
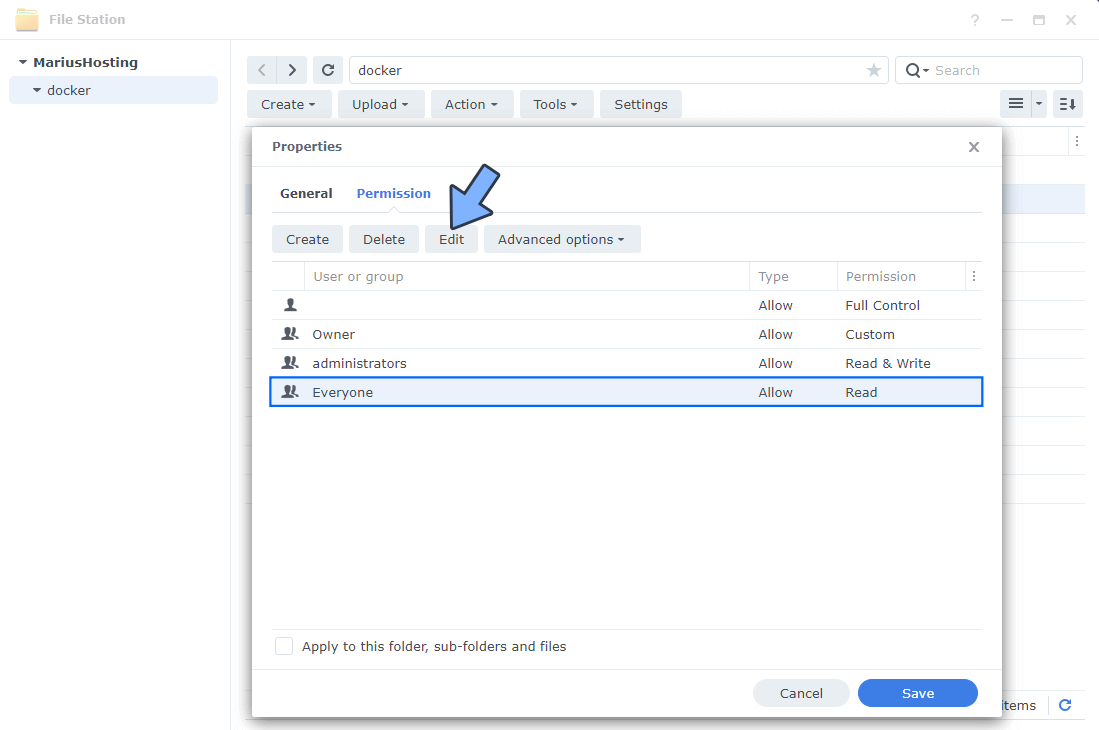
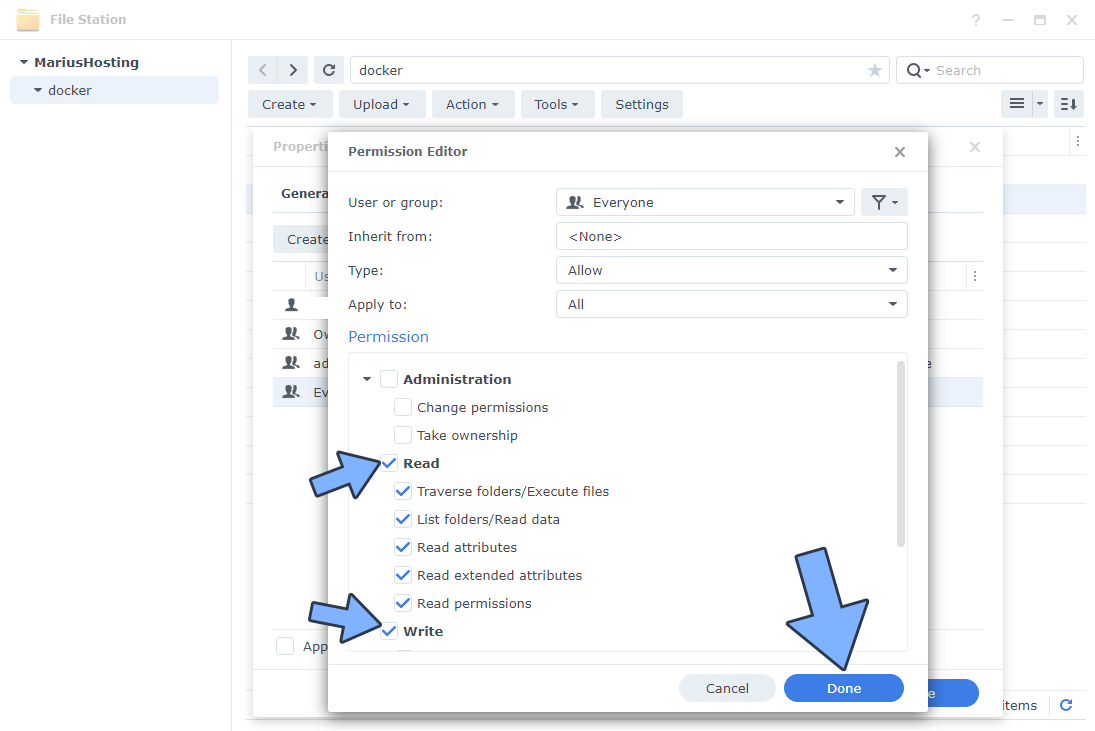
Select Everyone then click the Edit tab. Follow the instructions in the image below.
STEP 7
Check all Read and Write Permissions. Click Done. Follow the instructions in the image below.
STEP 8
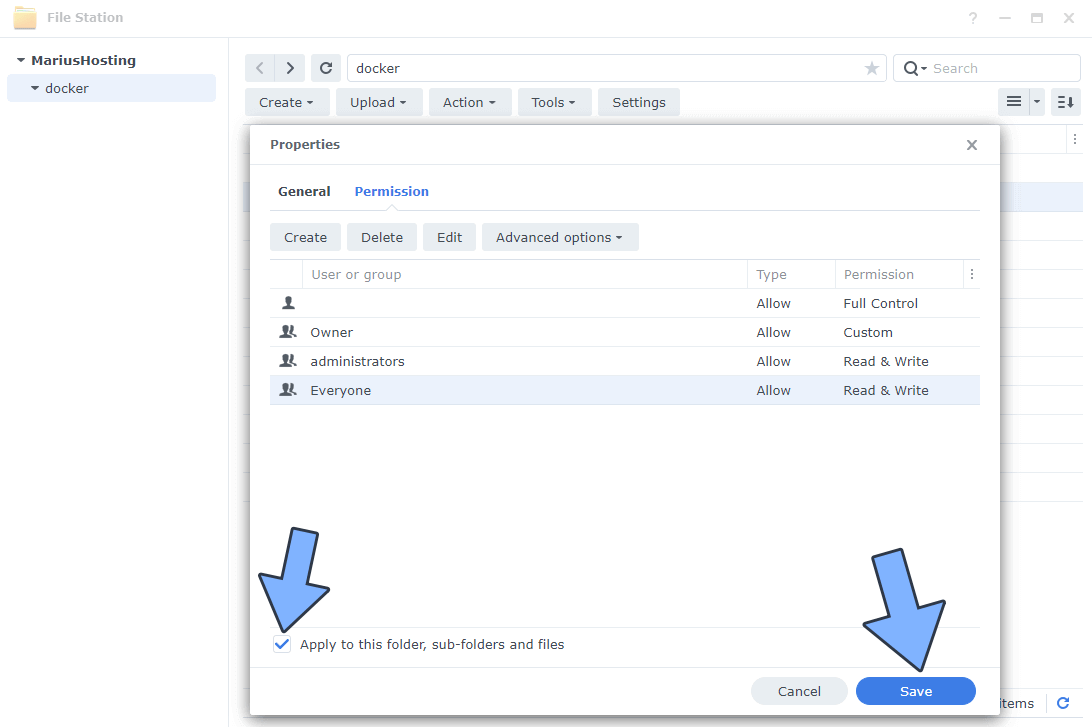
After you click Done on STEP 7, check “Apply to this folder, sub-folders and files“. Click Save. Follow the instructions in the image below.
STEP 9
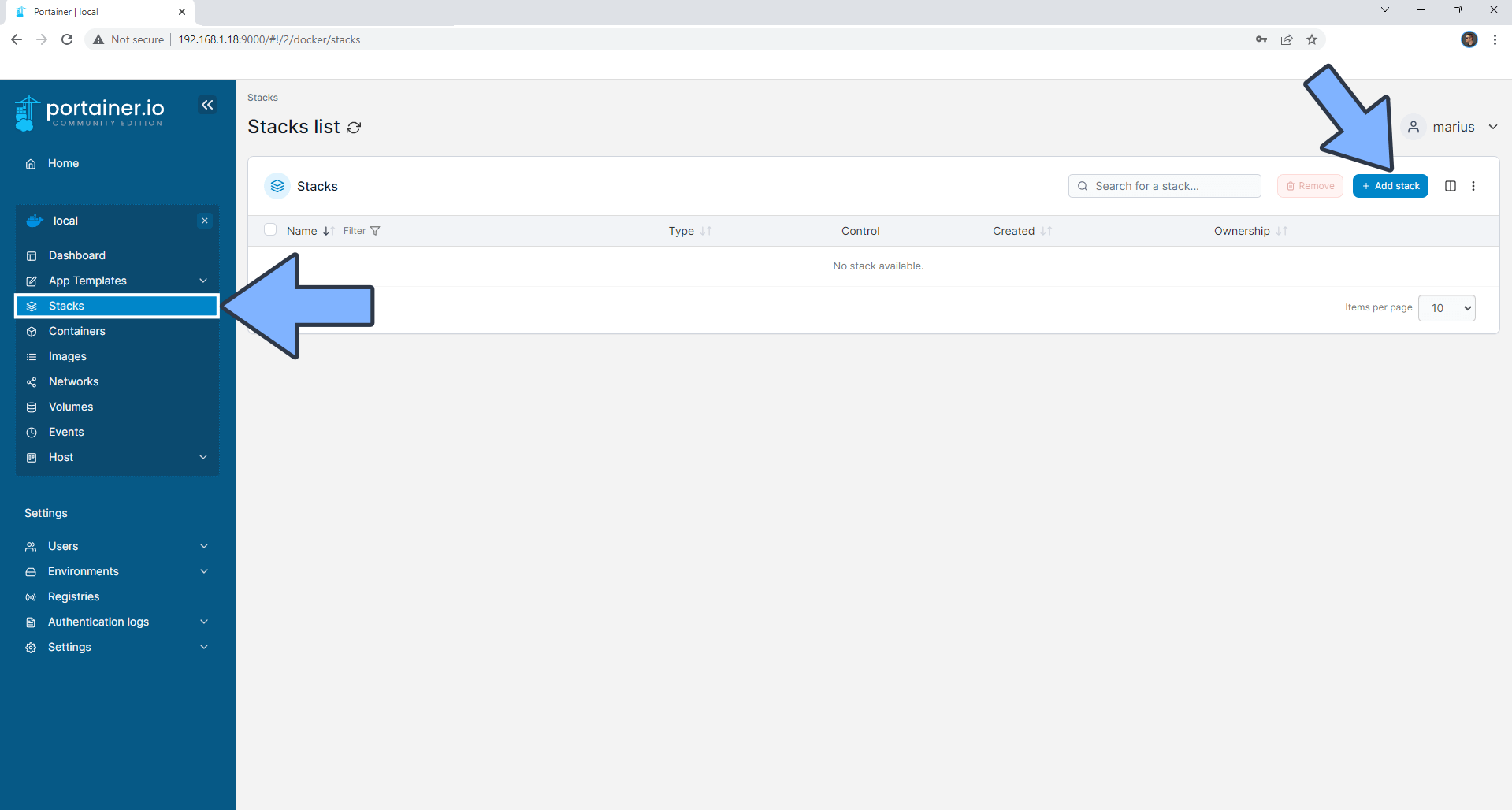
Log into Portainer using your username and password. On the left sidebar in Portainer, click on Stacks then + Add stack. Follow the instructions in the image below.
STEP 10
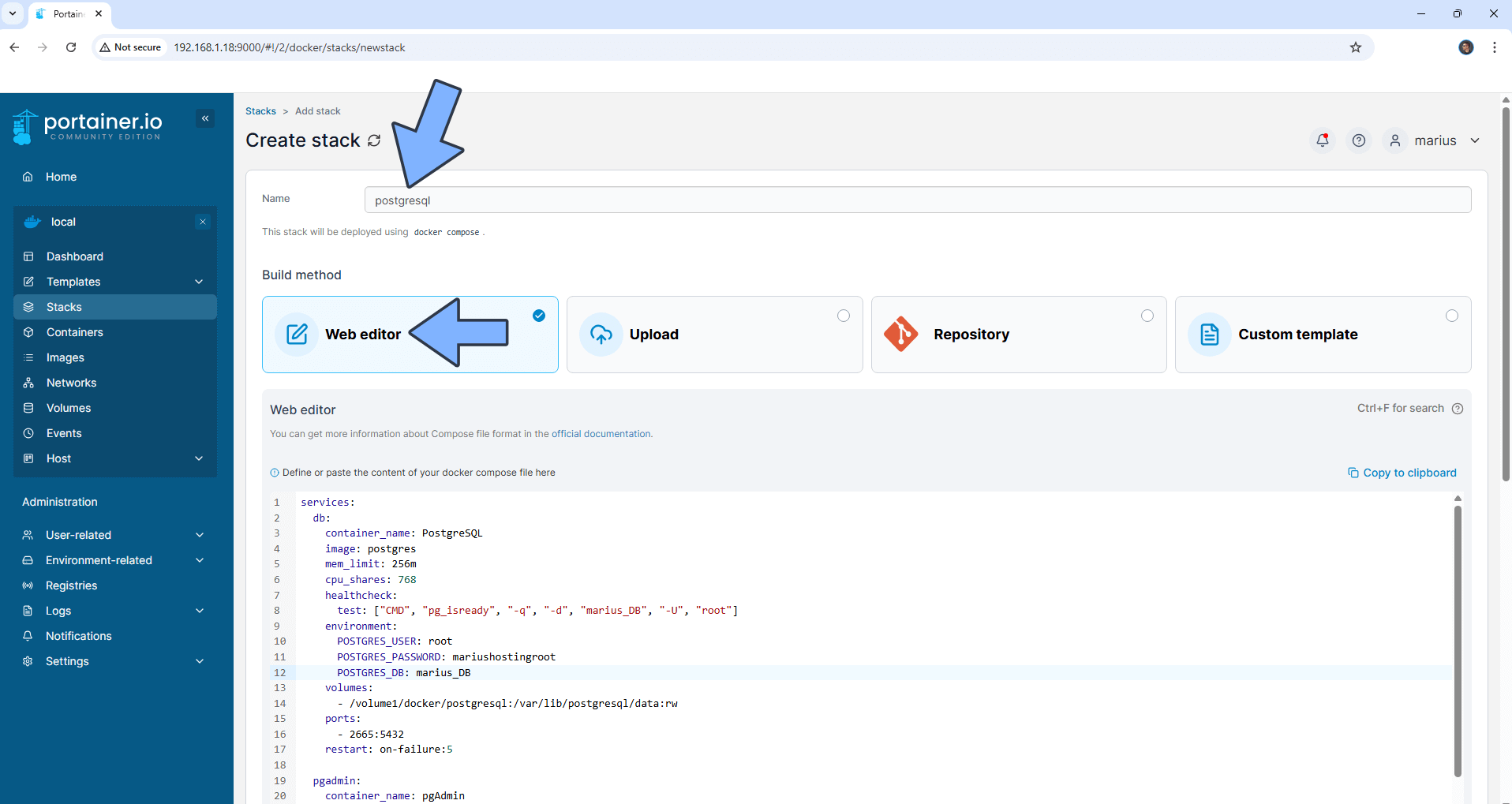
In the Name field type in postgresql. Follow the instructions in the image below.
services:
db:
container_name: PostgreSQL
image: postgres
mem_limit: 256m
cpu_shares: 768
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD", "pg_isready", "-q", "-d", "marius_DB", "-U", "root"]
environment:
POSTGRES_USER: root
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: mariushostingroot
POSTGRES_DB: marius_DB
volumes:
- /volume1/docker/postgresql:/var/lib/postgresql/data:rw
ports:
- 2665:5432
restart: on-failure:5
pgadmin:
container_name: pgAdmin
image: dpage/pgadmin4:latest
mem_limit: 256m
cpu_shares: 768
healthcheck:
test: wget --no-verbose --tries=1 --spider http://localhost:5050
environment:
PGADMIN_DEFAULT_EMAIL: Your-own-email@-address
PGADMIN_DEFAULT_PASSWORD: mariushosting
PGADMIN_LISTEN_PORT: 5050
ports:
- 2660:5050
volumes:
- /volume1/docker/postgresadmin:/var/lib/pgadmin:rw
restart: on-failure:5
Note: Before you paste the code above in the Web editor area below, change the value for POSTGRES_DB and type in your own database name. marius_DB is an example for a database name.
Note: Before you paste the code above in the Web editor area below, change the value for POSTGRES_PASSWORD and type in your own postgresql password. mariushostingroot is an example for a postgresql password.
Note: Before you paste the code above in the Web editor area below, change the value for PGADMIN_DEFAULT_EMAIL and type in your own email address.
Note: Before you paste the code above in the Web editor area below, change the value for PGADMIN_DEFAULT_PASSWORD and type in your own password. mariushosting is an example for a password.
STEP 11
Scroll down on the page until you see a button named Deploy the stack. Click on it. Follow the instructions in the image below. The installation process can take up to a few minutes. It will depend on your Internet speed connection.
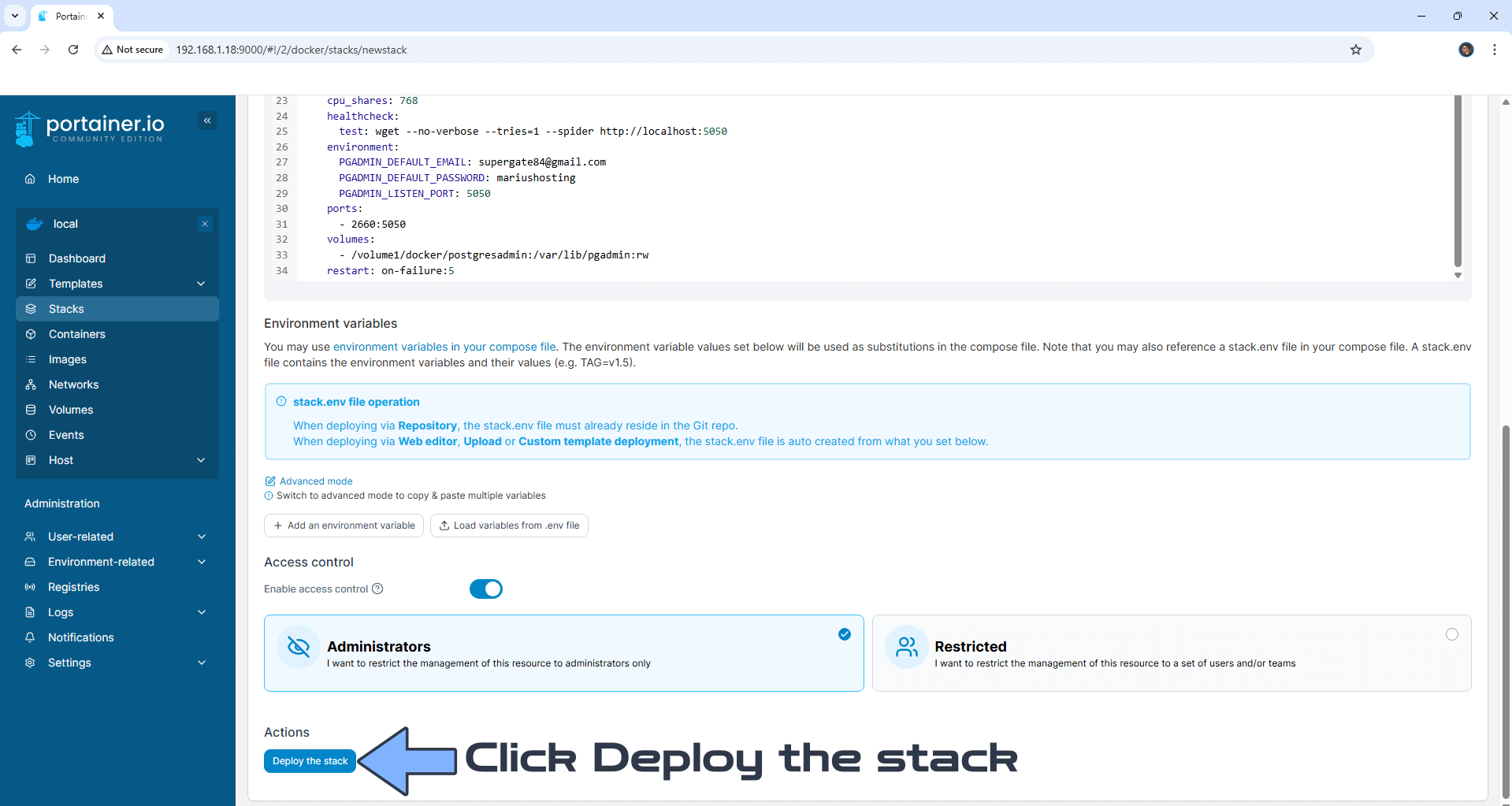
STEP 12
If everything goes right, you will see the following message at the top right of your screen: “Success Stack successfully deployed“.
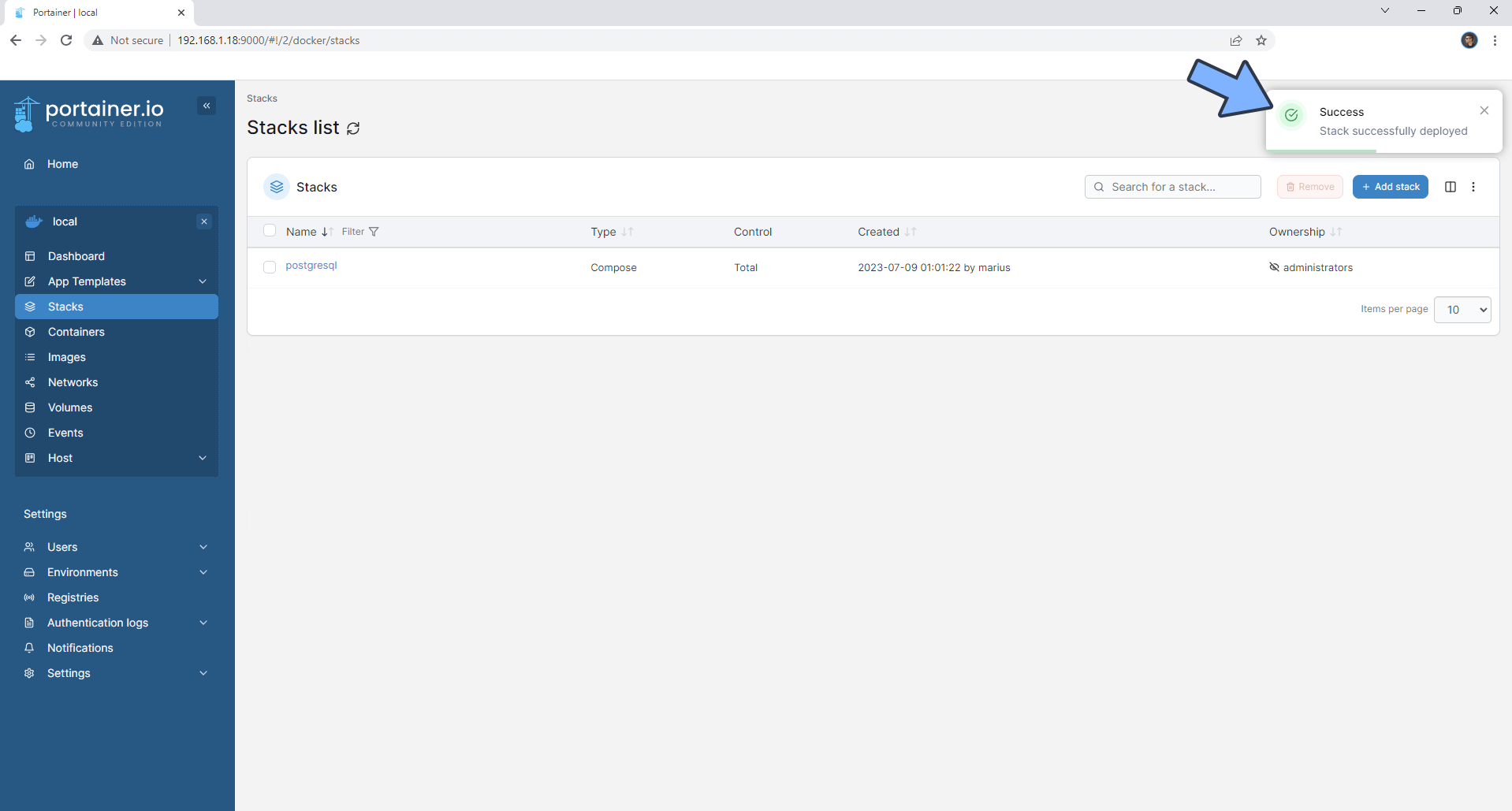
STEP 13
🟢Please Support My work by Making a Donation. Almost 99,9% of the people that install something using my guides forget to support my work, or just ignore STEP 1. I’ve been very honest about this aspect of my work since the beginning: I don’t run any ADS, I don’t require subscriptions, paid or otherwise, I don’t collect IPs, emails, and I don’t have any referral links from Amazon or other merchants. I also don’t have any POP-UPs or COOKIES. I have repeatedly been told over the years how much I have contributed to the community. It’s something I love doing and have been honest about my passion since the beginning. But I also Need The Community to Support me Back to be able to continue doing this work.
STEP 14
Please wait approximately 2 minutes for the installation to be completed or you will get a blank page if you try to connect too soon. Now open your browser and type in http://Synology-ip-address:2660 Type in your own Email Address and your PGADMIN_DEFAULT_PASSWORD that you have previously created at STEP 10. Choose your Language then click Login. Follow the instructions in the image below.
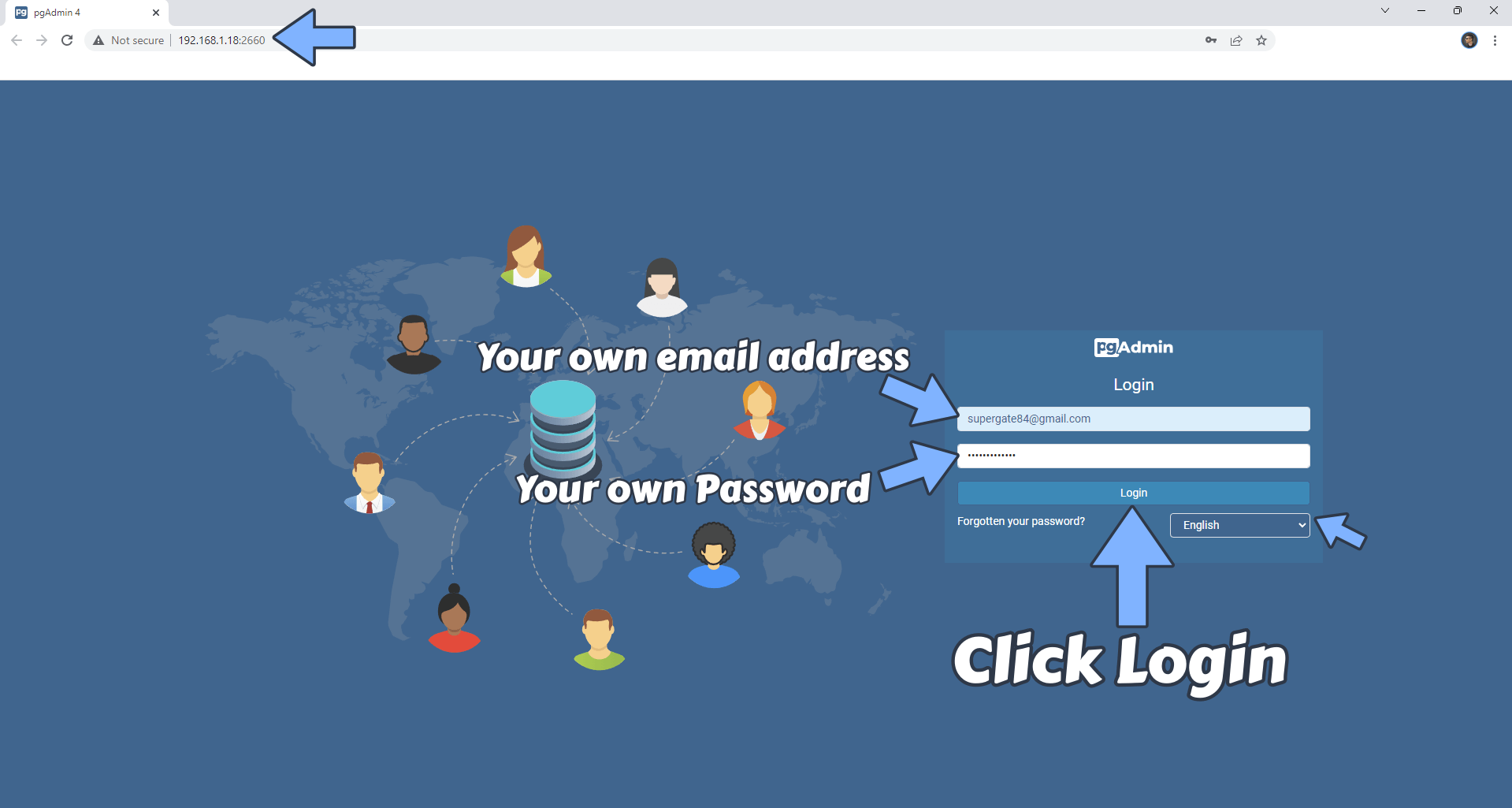
STEP 15
On the left sidebar, right click on Servers then Register then Server. Follow the instructions in the image below.
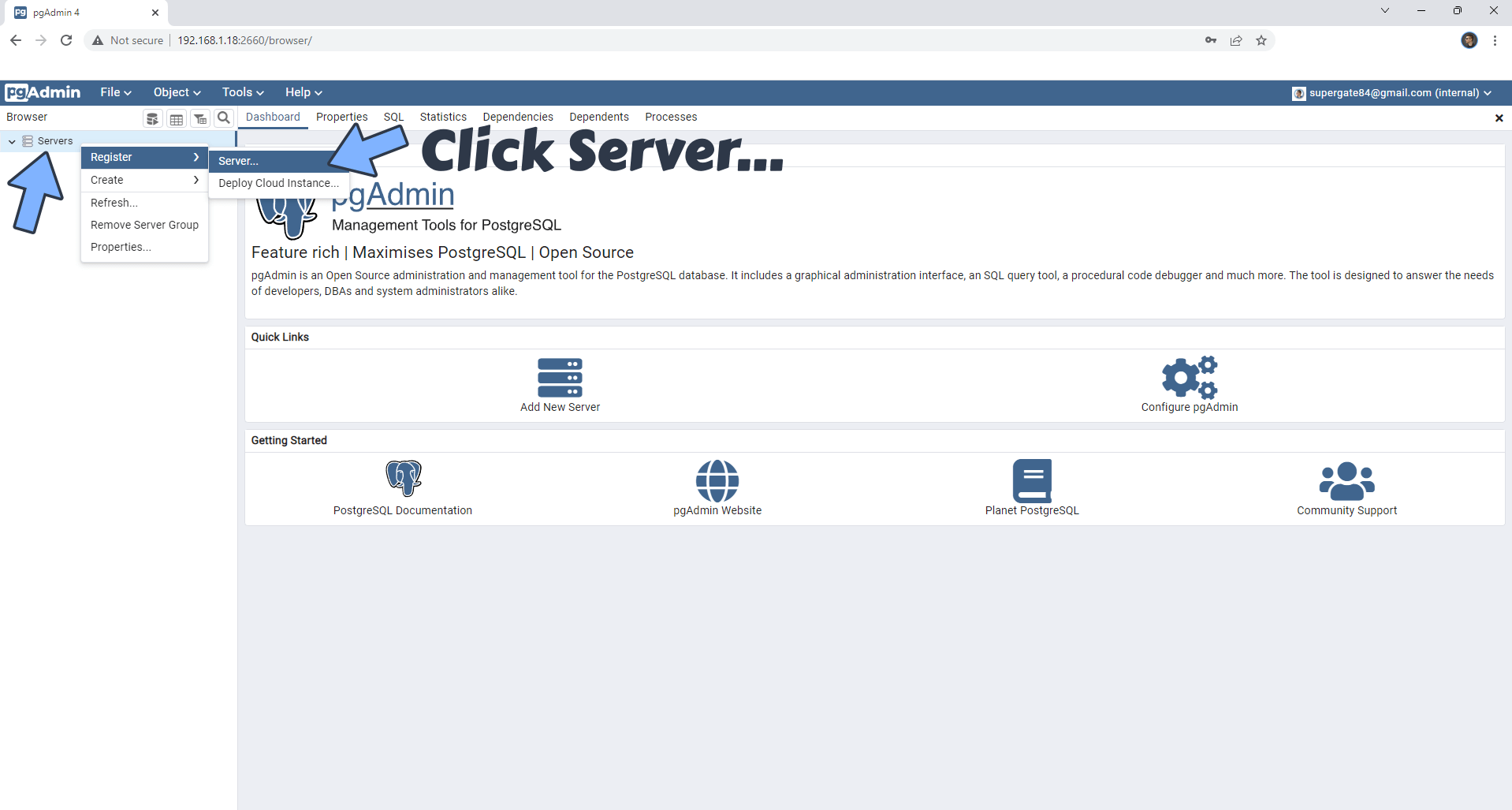
STEP 16
On the General tab area under Name type in Synology. Follow the instructions in the image below.
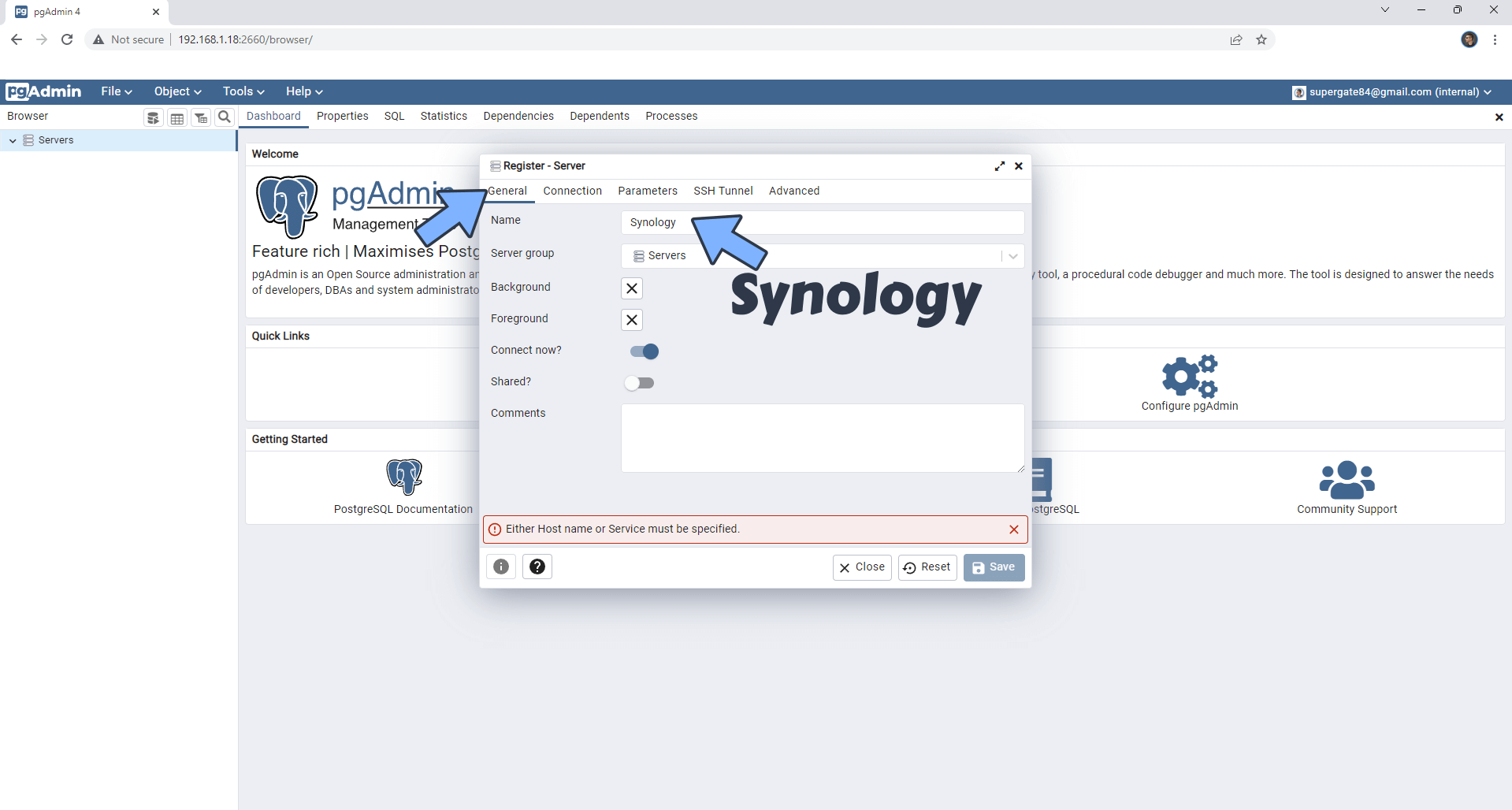
STEP 17
Click on the next tab Connection and add the details below then click Save.
Host name/address: PostgreSQL
Port: 5432
Maintenance database: postgres
Username: root
Password: Type in your own POSTGRES_PASSWORD that you have previously created at STEP 10.
Save Password: Yes
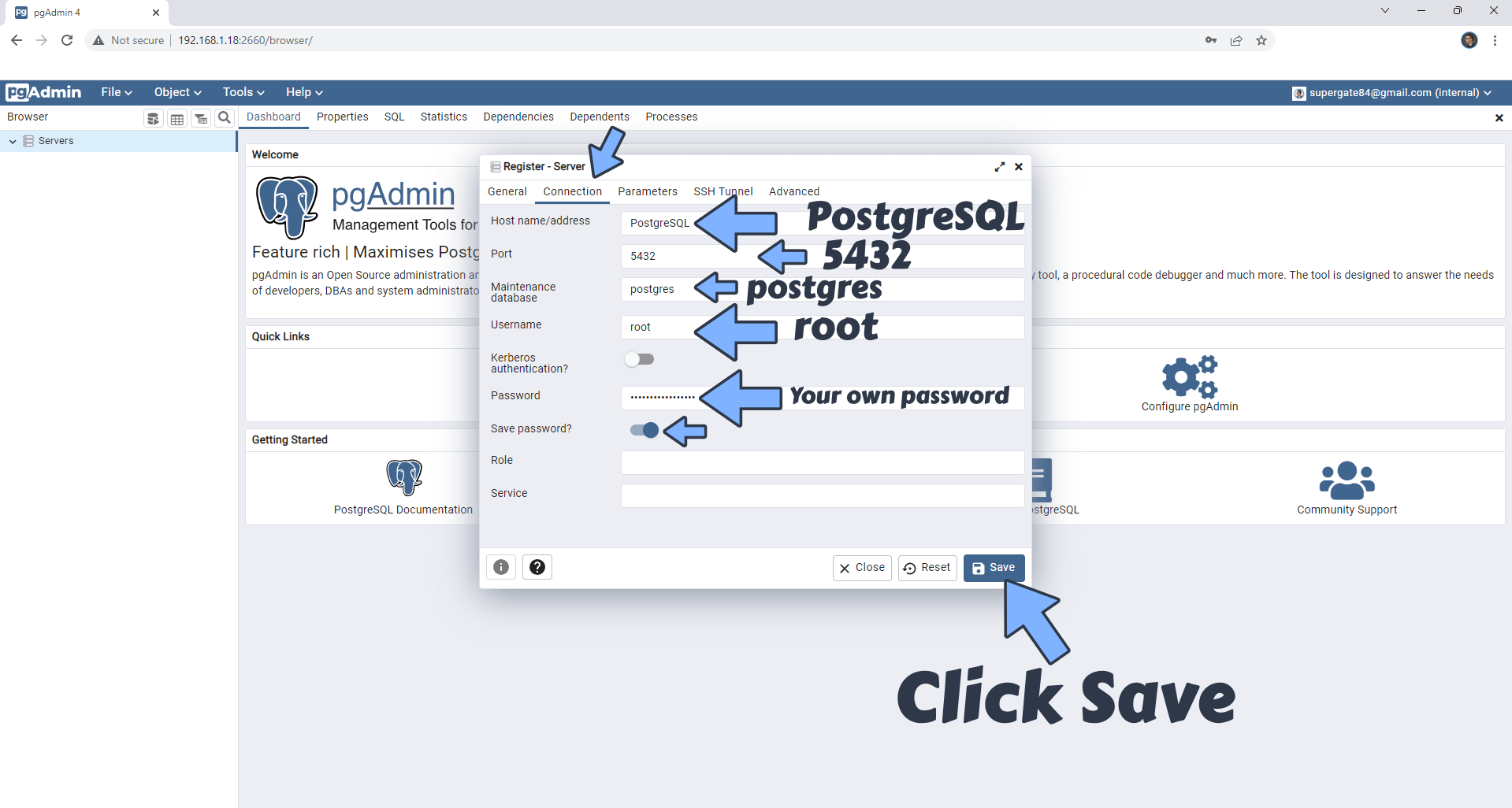
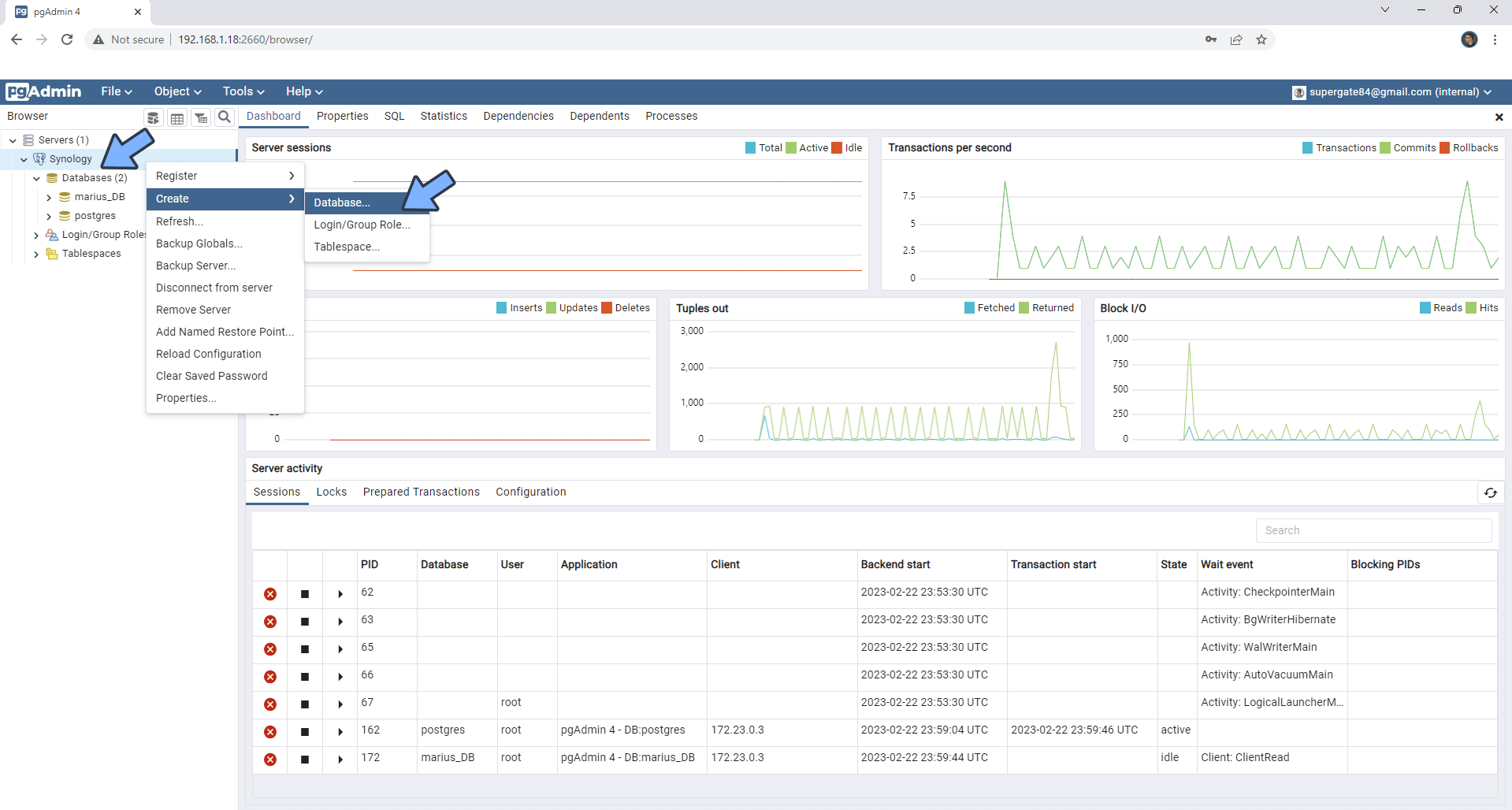
STEP 18
On the left sidebar right click on Synology. You can now create Databases, Users etc. Follow the instructions in the image below.
Enjoy PostgreSQL!
Note: Can I run Docker on my Synology NAS? See the supported models.
Note: How to Back Up Docker Containers on your Synology NAS.
Note: Find out how to update the PostgreSQL container with the latest image.
Note: How to Free Disk Space on Your NAS if You Run Docker.
Note: How to Schedule Start & Stop For Docker Containers.
Note: How to Activate Email Notifications.
Note: How to Add Access Control Profile on Your NAS.
Note: How to Change Docker Containers Restart Policy.
Note: How to Use Docker Containers With VPN.
Note: Convert Docker Run Into Docker Compose.
Note: How to Clean Docker.
Note: How to Clean Docker Automatically.
Note: Best Practices When Using Docker and DDNS.
Note: Some Docker Containers Need WebSocket.
Note: Find out the Best NAS Models For Docker.
Note: Activate Gmail SMTP For Docker Containers.
This post was updated on Thursday / May 22nd, 2025 at 10:33 AM
