
If you use your Synology NAS as an FTP server, for Web Hosting, intensive File Sharing, or you run VMs on your NAS, or your NAS acts as a Virtual Machine storage, or anything that requires continual and systematic retrieval of data, you will benefit extensively from using the M.2 NVMe SSD Cache. M.2 NVMe SSD is intended for use as a cache drive for systems using an HDD mechanical hard drive or 2.5″ SATA SSDs for primary storage. The data that is frequently or recently used on your Synology NAS can be accessed more quickly from the cache devices (M.2 NVMe SSD) than from the larger, comparatively slower HDD/SSD devices. So basically, the NVMe SSDs borrow frequently or recently used data from primary HDDs/SATA SSDs and cache it. Said data will then be accessed from them by means of a higher read/write performance.
What is M.2? M.2 is merely a connector which plugs into the PCIe bus interface.
What is NVMe? NVM Express or Non-Volatile Memory Host Controller Interface Specification is an open logical device interface specification for accessing non-volatile storage media attached via PCIe bus.
- Read-only cache: When you set only one M.2 NVMe SSD as the read-only cache, only frequently accessed data is stored in the cache to accelerate random read speeds. Because it’s not involved in writing data, data will remain safe and sound even when the SSD breaks down.
- Read-write cache: Compared to the read-only cache, the read-write cache writes data synchronously to the M.2 NVMe SSD. To ensure data safety, you need at least two M.2 NVMe SSDs to set up RAID 1 to allow fault tolerance of one SSD. But there’s still a risk of data loss if the number of worn-out SSDs exceeds the fault tolerance in a RAID configuration.
When accessing data from cache, you’ll get SSD-like (M.2 NVMe SSD) performance. Have you ever wondered why this website is so fast? Well, mariushosting.com uses two SNV3400-400G Synology drives for cache acceleration. Thanks to their sequential read speed of 3100MB/s, the two M.2 NVMe SSD discs enhance the sequential read speed of my current Synology SAT5200 SATA SSD disks data.
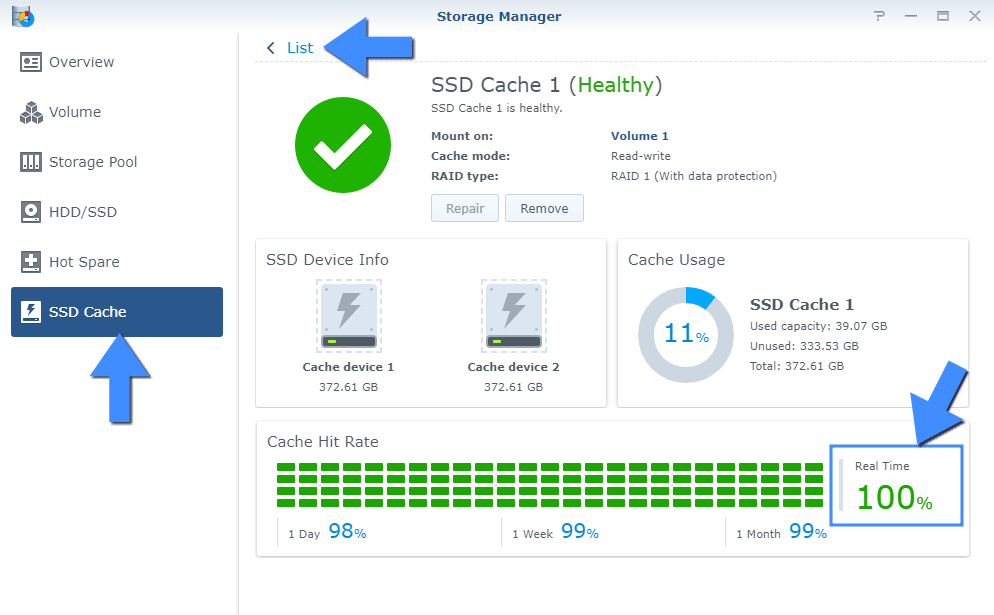
Note: Find out where is Cache Hit Rate in Synology DSM 7.
As you can see, this website is hosted from home on a DS720+ Synology NAS. Whenever you visit this site, images, text, html, codes, and any and all data that are viewed frequently by visitors are directly taken from the M.2 NVMe SSD cache disks instead of my internal SATA 2.5″ SSD disks. I have always had a Real Time Cache Hit-Rate of 100%.
What happens when M.2 NVMe SSD Cache gets full? When this happens, it will start removing the oldest and least-used data in favor of newer or frequently-used data. But once it fills up (100%), it may always look “full” because it’s always swapping data around. That’s how data caching works. But there’ll be no performance decrease.
To better understand the process, my current SAT5200-480G SATA discs have a sequential read speed of 530MB/s and a sequential write speed of 500MB/s. I am using two M.2 NVMe SSD discs as cache and, in my case, the sequential read speed is up to 3100MB/s and the sequential write speed is 550MB/s. So my visitors will be able to access data from my website 6 times faster. The data that is continuously accessed by visitors will be automatically retrieved from cache.
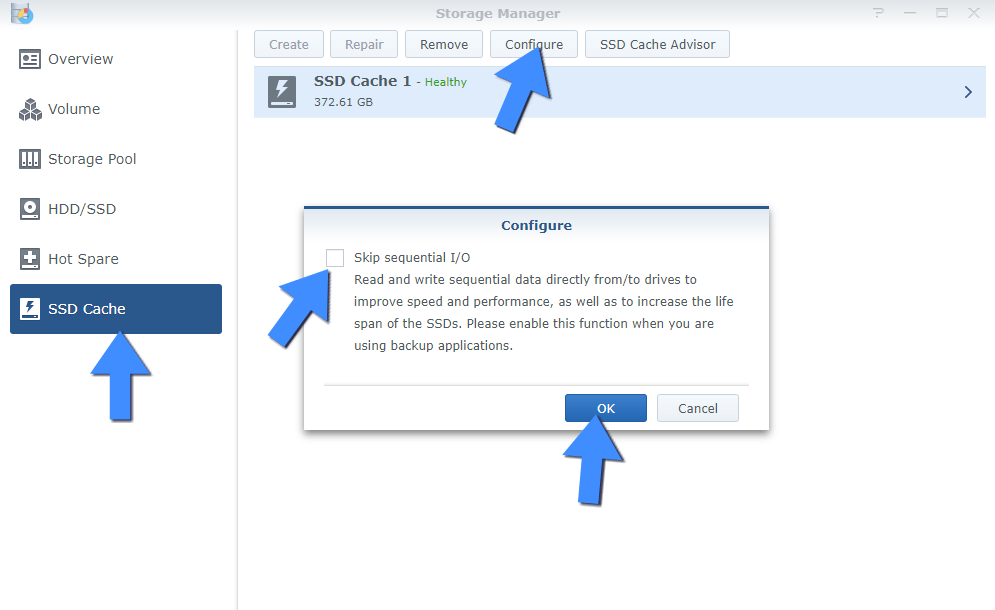
If you are hosting a website from home on your own Synology NAS and want to speed up access to your site and enjoy all the speed performance your M.2 NVMe SSD discs can offer, remember to uncheck the option Skip sequential I/O automatically checked by the system in Storage Manager. By default, sequential access is skipped, meaning reads/writes for large files will go directly to your HDDs or SATA 2.5″ SSDs. Follow the instructions in the image below.
Note: Cache management uses RAM, approximately 416 KB for every 1 GB of SSD cache. A read-only cache with two 128 GB SSDs is 256 GB, requiring at least 104 MB of memory. A read-write cache with the same drives requires at least 52 MB of memory.
Note: If you are primarily storing videos on your primary discs, then you will not benefit from M.2 NVMe SSD cache. Loading speeds for DS Audio, Video Station, Plex will most likely not be improved in a significant manner, though it may depend on the amount of files you have, the average file size, and number of clients.
Note: If you run a Plex server, M.2 NVMe SSD Cache can’t do much to improve experience.
Note: Upcoming DSM 7 improving SSD cache application. In response to the fast-growing use of the SSD cache application, Synology has significantly updated DSM support for SSD cache. The new SSD cache recommendation will analyze I/O mode in a more precise manner, providing users with the most cost-effective SSD based on actual usage & capacity. There’s also support for locking relay data to SSDs to significantly improve system operation efficiency involving cold relay data.
This post was updated on Tuesday / August 30th, 2022 at 7:59 AM
