Did you know that Synology offers a free tool named RAID Calculator? Synology’s RAID Calculator tool can provide an estimate on space utilization with various mixed HDD/SSD configurations and RAID types. If you have a Synology NAS, you can choose a different RAID type on your HDD or SSD disks. For those who don’t know, RAID is the acronym for Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks, the purpose of which is to give you varying degrees of resilience by copying/spreading the data from a disk to one or more other disks. If one drive fails, the system is able to keep operating, using the remaining drive(s) while you organize a disk swap. The data storage virtualization technology combines multiple physical disk drive components into one or more logical units for the purposes of data redundancy, performance improvement, or both.
Once you access the Synology website via the link above, you will find yourself in front of this extremely well-organized tool where you will be asked to choose the number of disks and their capacity. You can quickly and easily choose different RAID types and, at the end, you will even be shown a recommended product.
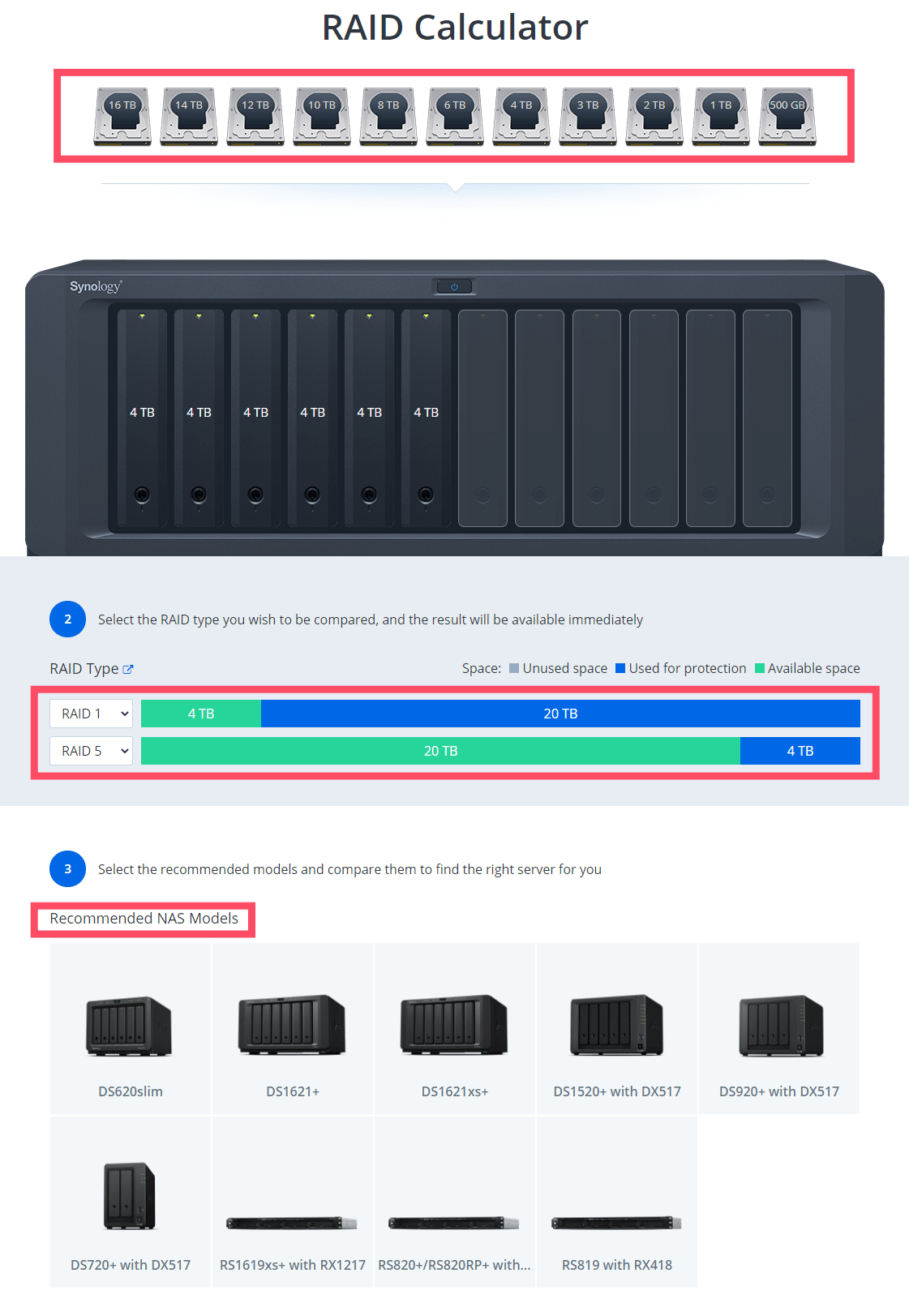
The following RAID levels may be available on your Synology NAS
- Basic Composed of one drive as an independent unit. Does not provide data redundancy.
- JBOD Combines a collection of drives into a single storage space, with capacity equal to the sum of all drives’ capacity. Does not provide data redundancy. You can use it with just 1 disk.
- RAID 0 Features “striping,” a process of dividing data into blocks and spreading the data blocks across several drives in order to enhance performance. Does not provide data redundancy.
- RAID 1 Writes identical data to both drives simultaneously and provides data redundancy.
- RAID 5 Implements block-level striping with parity data distributed across all member drives, thus providing data redundancy more efficiently than RAID 1, but you need a minimum of 3 disks.
- RAID 6 Implements two layers of data parity to store redundant data equal to the size of two drives, providing a greater degree of data redundancy than RAID 5, but you need a minimum of 4 disks.
- RAID 10 Provides the performance of RAID 0 and data protection level of RAID 1, combining drives into groups of two in which data is mirrored, but you need a minimum of 4 disks.
- RAID F1 Implements block-level striping with parity data distributed across all member drives. Writes more parity information on a certain drive. Recommended for an all-flash array.
If you don’t have the technical expertise to differentiate between the different RAID types to suit your use, Synology has you covered with Synology Hybrid Raid (SHR):
- SHR optimizes volume size when combining drives of different sizes. It provides data redundancy if the volume is composed of two or more drives. Recommended for beginners.
Synology SHR is an automated RAID management system that makes storage volume deployment easier than traditional RAID systems. SHR will allow users to handle RAID management, expand storage and maximize storage capability, and meet the needs of new users who are unfamiliar with RAID types. SHR allows for 1-disk or 2-disk worth of redundancy, meaning the SHR volume can suffer up to two disks lost, and the data volume will still be available for use. Note: A RAID volume (either Classic RAID or SHR) is not a backup system.
Note: The online Synology RAID Calculator tool makes recommendations based on the total capacity picked. Some models or configurations may not support a certain capacity drive, but will be able to achieve the total capacity through other combinations or when paired with an expansion unit.
Note: The data storage virtualization technology combines multiple physical disk drive components into one or more logical units for the purposes of data redundancy, performance improvement, or both.
Note: When using SHR or SHR-2 HDD protection as your RAID type, the unused space will be automatically reserved for future expansion. On the contrary, unused space under other RAID types indicates the space that can’t be utilized and is thus wasted.
Note: RAID is NOT a backup. RAID provides dynamic resilience so that your system can continue to run if a drive fails by falling back on the other disks in the RAID. If data is accidentally deleted or modified, those changes are mirrored too. RAID is therefore not a backup service. Don’t confuse resilience with a backup archive – they are very different. You need a backup strategy.
Note: Avoid RAID 0 or Single Disk SHR. Data on a single disk that is not mirrored is vulnerable. Don’t put data on a single disk unless you can afford to lose it. For example, if I were to have my entry web hosting onto a single drive, I couldn’t afford to lose the disk because I would lose all the data.
Note: Can I change the RAID type after I have already set one? A RAID type can only be changed by adding one or more disks. Storage pools can be changed from one RAID type to another without losing existing data.
This post was updated on Wednesday / August 10th, 2022 at 10:10 PM
